Deciphering diseases and biological targets for environmental chemicals using toxicogenomics networks
- PMID: 20502671
- PMCID: PMC2873901
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000788
Deciphering diseases and biological targets for environmental chemicals using toxicogenomics networks
Abstract
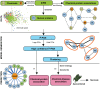
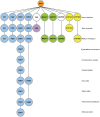
Exposure to environmental chemicals and drugs may have a negative effect on human health. A better understanding of the molecular mechanism of such compounds is needed to determine the risk. We present a high confidence human protein-protein association network built upon the integration of chemical toxicology and systems biology. This computational systems chemical biology model reveals uncharacterized connections between compounds and diseases, thus predicting which compounds may be risk factors for human health. Additionally, the network can be used to identify unexpected potential associations between chemicals and proteins. Examples are shown for chemicals associated with breast cancer, lung cancer and necrosis, and potential protein targets for di-ethylhexyl-phthalate, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, pirinixic acid and permethrine. The chemical-protein associations are supported through recent published studies, which illustrate the power of our approach that integrates toxicogenomics data with other data types.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Edwards TM, Myers JP. Environmental exposures and gene regulation in disease etiology. Cien saude Colet. 2008;13:269–281. - PubMed
-
- Phillips DH, Arlt VM. Genotoxicity: damage to DNA and its consequences. EXS. 2009;99:87–110. - PubMed
-
- Paolini GV, Shapland RH, van Hoorn WP, Mason JS, Hopkins AL. Global mapping of pharmacological space. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:805–815. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1110–1111. - PubMed
-
- Yildirim MA, Goh KI, Cusick ME, Barabasi AL, Vidal M. Drug-target network. Nat Biotechno. 2007;l 25:1119–1126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

