Mutation in archain 1, a subunit of COPI coatomer complex, causes diluted coat color and Purkinje cell degeneration
- PMID: 20502676
- PMCID: PMC2873907
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000956
Mutation in archain 1, a subunit of COPI coatomer complex, causes diluted coat color and Purkinje cell degeneration
Abstract
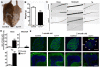
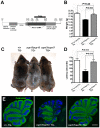
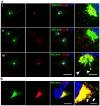
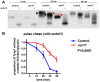
Intracellular trafficking is critical for delivering molecules and organelles to their proper destinations to carry out normal cellular functions. Disruption of intracellular trafficking has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative disorders. In addition, a number of genes involved in vesicle/organelle trafficking are also essential for pigmentation, and loss of those genes is often associated with mouse coat-color dilution and human hypopigmentary disorders. Hence, we postulated that screening for mouse mutants with both neurological defects and coat-color dilution will help identify additional factors associated with intracellular trafficking in neuronal cells. In this study, we characterized a mouse mutant with a unique N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-induced mutation, named nur17. nur17 mutant mice exhibit both coat-color dilution and ataxia due to Purkinje cell degeneration in the cerebellum. By positional cloning, we identified that the nur17 mouse carries a T-to-C missense mutation in archain 1 (Arcn1) gene which encodes the delta subunit of the coat protein I (COPI) complex required for intracellular trafficking. Consistent with this function, we found that intracellular trafficking is disrupted in nur17 melanocytes. Moreover, the nur17 mutation leads to common characteristics of neurodegenerative disorders such as abnormal protein accumulation, ER stress, and neurofibrillary tangles. Our study documents for the first time the physiological consequences of the impairment of the ARCN1 function in the whole animal and demonstrates a direct association between ARCN1 and neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Schwartz AL. Cell biology of intracellular protein trafficking. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:195–229. - PubMed
-
- Annaert W, De Strooper B. A cell biological perspective on Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:25–51. - PubMed
-
- Uemura K, Kuzuya A, Shimohama S. Protein trafficking and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2004;1:1–10. - PubMed
-
- DiFiglia M, Sapp E, Chase K, Schwarz C, Meloni A, et al. Huntingtin is a cytoplasmic protein associated with vesicles in human and rat brain neurons. Neuron. 1995;14:1075–1081. - PubMed
-
- Gil JM, Rego AC. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2803–2820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

