Soluble isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor are predictors of response to sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinomas
- PMID: 20502715
- PMCID: PMC2873294
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010715
Soluble isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor are predictors of response to sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinomas
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis is the target of several agents in the treatment of malignancies, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC). There is a real need for surrogate biomarkers that can predict selection of patients who may benefit from antiangiogenic therapies, prediction of disease outcome and which may improve the knowledge regarding mechanism of action of these treatments. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) have proven efficacy in metastatic RCC (mRCC). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the clinical response to these drugs remain unclear.
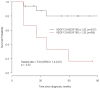
Methodology/principal findings: The present study aimed to identify molecular biomarkers associated with the response to sunitinib, a Tyrosine kinase inhibitor. To evaluate this relationship, primary tumors from 23 metastatic RCC patients treated by sunitinib were analyzed for a panel of 16 biomarkers involved in tumor pathways targeted by sunitinib, using real-time quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR. Nine of the 23 patients (39%) responded to sunitinib. Among transcripts analyzed, only the levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) soluble isoforms (VEGF(121) and VEGF(165)) were associated with the response to sunitinib (P = 0.04 for both). Furthermore, the ratio of VEGF soluble isoforms (VEGF(121)/VEGF(165)) was significantly associated with prognosis (P = 0.02).
Conclusions: This preliminary study provides a promising tool that might help in the management of metastatic RCC, and could be extended to other tumors treated by TKI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of tissue microRNAs predictive of sunitinib activity in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 24;9(1):e86263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086263. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475095 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy for the treatment of adult metastatic Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2010 Nov 15;116(22):5219-25. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25512. Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20665500 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating protein biomarkers of pharmacodynamic activity of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: modulation of VEGF and VEGF-related proteins.J Transl Med. 2007 Jul 2;5:32. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-5-32. J Transl Med. 2007. PMID: 17605814 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improvement in survival end points of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma through sequential targeted therapy.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Nov;50:109-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 27664394 Review.
-
Biomarkers to predict response to sunitinib therapy and prognosis in metastatic renal cell cancer.Cancer Sci. 2011 Nov;102(11):1949-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02054.x. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21812860 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and predictive value of VHL gene alteration in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis and review.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13979-13985. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14704. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28103578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Paracrine Signaling by Sunitinib-Resistant Renal Cell Carcinoma.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Jun 15;36(13):1836-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00189-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27141054 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the vasculature of tumours: combining VEGF pathway inhibitors with radiotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2019 Jan;92(1093):20180405. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180405. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30160184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyses of potential predictive markers and survival data for a response to sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 27;8(9):e76386. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076386. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24086736 Free PMC article.
-
Active angiogenesis in metastatic renal cell carcinoma predicts clinical benefit to sunitinib-based therapy.Br J Cancer. 2014 May 27;110(11):2700-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.225. Epub 2014 May 1. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24786599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Small EJ. Biology and clinical development of vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1028–1043. - PubMed
-
- Amato RJ. Renal cell carcinoma: review of novel single-agent therapeutics and combination regimens. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:7–15. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–660. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

