Clinical significance of early (< 20 weeks) vs. late (20-24 weeks) detection of sonographic short cervix in asymptomatic women in the mid-trimester
- PMID: 20503224
- PMCID: PMC2937193
- DOI: 10.1002/uog.7673
Clinical significance of early (< 20 weeks) vs. late (20-24 weeks) detection of sonographic short cervix in asymptomatic women in the mid-trimester
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine whether the risk of early spontaneous preterm delivery (PTD) in asymptomatic women with a sonographic cervical length of ≤ 15 mm in the mid-trimester changes as a function of gestational age at diagnosis.
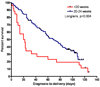
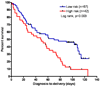
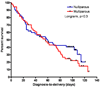
Methods: This cohort study included 109 asymptomatic patients with a sonographic cervical length of ≤ 15 mm diagnosed at 14-24 weeks of gestation. Women with a multifetal gestation, cerclage and a cervical dilatation of > 2 cm were excluded. The study population was stratified by gestational age at diagnosis (< 20 weeks vs. 20-24 weeks) and by cervical length (≤ 10 mm vs. 11-15 mm). The primary outcome variables were PTD at < 28 and < 32 weeks of gestation and the diagnosis-to-delivery interval.
Results: The median gestational age at diagnosis of a short cervix before 20 weeks and at 20-24 weeks was 18.9 and 22.7 weeks, respectively. Women diagnosed before 20 weeks had a higher rate of PTD at < 28 weeks (76.9% vs. 30.9%; P < 0.001) and at < 32 weeks (80.8% vs. 48.1%; P = 0.004), and a shorter median diagnosis-to-delivery interval (21 vs. 61.5 days, P = 0.003) than those diagnosed at 20-24 weeks. The rate of amniotic fluid sludge was higher among patients diagnosed with a short cervix at < 20 weeks of gestation than in those in whom it was diagnosed between 20 and 24 weeks (92.3% vs. 48.2%; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Asymptomatic women with a sonographic cervical length of ≤ 15 mm diagnosed before 20 weeks of gestation have a dramatic and significantly higher risk of early preterm delivery than women diagnosed at 20-24 weeks. These findings can be helpful to physicians in counseling these patients, and may suggest different mechanisms of disease leading to a sonographic short cervix before or after 20 weeks of gestation.
Copyright © 2010 ISUOG. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen HF, Nugent CE, Wanty SD, Hayashi RH. Prediction of risk for preterm delivery by ultrasonographic measurement of cervical length. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;163:859–867. - PubMed
-
- Iams JD, Goldenberg RL, Meis PJ, Mercer BM, Moawad A, Das A, Thom E, McNellis D, Copper RL, Johnson F, Roberts JM. The length of the cervix and the risk of spontaneous premature delivery. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:567–572. - PubMed
-
- Heath VC, Southall TR, Souka AP, Elisseou A, Nicolaides KH. Cervical length at 23 weeks of gestation: prediction of spontaneous preterm delivery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1998;12:312–317. - PubMed
-
- Hassan SS, Romero R, Berry SM, Dang K, Blackwell SC, Treadwell MC, Wolfe HM. Patients with an ultrasonographic cervical length < or =15 mm have nearly a 50% risk of early spontaneous preterm delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:1458–1467. - PubMed
-
- Tekesin I, Eberhart LH, Schaefer V, Wallwiener D, Schmidt S. Evaluation and validation of a new risk score (CLEOPATRA score) to predict the probability of premature delivery for patients with threatened preterm labor. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;26:699–706. - PubMed

