Morphology and mosaics of melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cell types in mice
- PMID: 20503419
- PMCID: PMC2895505
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22381
Morphology and mosaics of melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cell types in mice
Abstract
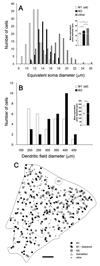
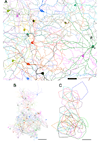
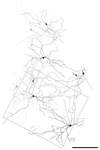
Melanopsin is the photopigment of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs). Melanopsin immunoreactivity reveals two dendritic plexuses within the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and morphologically heterogeneous retinal ganglion cells. Using enhanced immunohistochemistry, we provide a fuller description of murine cell types expressing melanopsin, their contribution to the plexuses of melanopsin dendrites, and mosaics formed by each type. M1 cells, corresponding to the originally described ganglion-cell photoreceptors, occupy the ganglion cell or inner nuclear layers. Their large, sparsely branched arbors (mean diameter 275 microm) monostratify at the outer limit of the OFF sublayer. M2 cells also have large, monostratified dendritic arbors (mean diameter 310 microm), but ramify in the inner third of the IPL, within the ON sublayer. There are approximately 900 M1 cells and 800 M2 cells per retina; each type comprises roughly 1-2% of all ganglion cells. The cell bodies of M1 cells are slightly smaller than those of M2 cells (mean diameters: 13 microm for M1, 15 microm for M2). Dendritic field overlap is extensive within each type (coverage factors approximately 3.8 for M1 and 4.6 for M2 cells). Rare bistratified cells deploy terminal dendrites within both melanopsin-immunoreactive plexuses. Because these are too sparsely distributed to permit complete retinal tiling, they lack a key feature of true ganglion cell types and may be anomalous hybrids of the M1 and M2 types. Finally, we observed weak melanopsin immunoreactivity in other ganglion cells, mostly with large somata, that may constitute one or more additional types of melanopsin-expressing cells.
Figures



References
-
- Badea TC, Nathans J. Quantitative analysis of neuronal morphologies in the mouse retina visualized by using a genetically directed reporter. J Comp Neurol. 2004;480(4):331–351. - PubMed
-
- Baver SB, Pickard GE, Sollars PJ. Two types of melanopsin retinal ganglion cell differentially innervate the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus and the olivary pretectal nucleus. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(7):1763–1770. - PubMed
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002;295(5557):1070–1073. - PubMed
-
- Coombs J, van der List D, Wang GY, Chalupa LM. Morphological properties of mouse retinal ganglion cells. Neuroscience. 2006;140(1):123–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

