A comparison of probe-level and probeset models for small-sample gene expression data
- PMID: 20504334
- PMCID: PMC2901368
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-281
A comparison of probe-level and probeset models for small-sample gene expression data
Abstract
Background: Statistical methods to tentatively identify differentially expressed genes in microarray studies typically assume larger sample sizes than are practical or even possible in some settings.
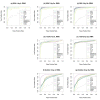
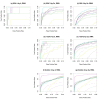
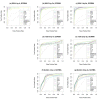
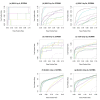
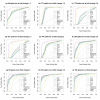
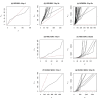
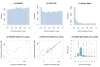
Results: The performance of several probe-level and probeset models was assessed graphically and numerically using three spike-in datasets. Based on the Affymetrix GeneChip, a novel nested factorial model was developed and found to perform competitively on small-sample spike-in experiments.
Conclusions: Statistical methods with test statistics related to the estimated log fold change tend to be more consistent in their performance on small-sample gene expression data. For such small-sample experiments, the nested factorial model can be a useful statistical tool. This method is implemented in freely-available R code (affyNFM), available with a tutorial document at http://www.stat.usu.edu/~jrstevens.
Figures


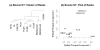
References
-
- Aston KI, Li GP, Hicks BA, Sessions BR, Pate BJ, Hammon DS, Bunch TD, White KL. Effect of the time interval between fusion and activation on nuclear state and development in vitro and in vivo of bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. Reproduction. 2006;131:45–51. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00714. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gentleman R, Huber W, Carey VJ, Irizarry RA, Dudoit S. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor. New York, Springer; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

