Zinc release from thapsigargin/IP3-sensitive stores in cultured cortical neurons
- PMID: 20504366
- PMCID: PMC2897781
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-5
Zinc release from thapsigargin/IP3-sensitive stores in cultured cortical neurons
Abstract
Background: Changes in ionic concentration have a fundamental effect on numerous physiological processes. For example, IP3-gated thapsigargin sensitive intracellular calcium (Ca2+) storage provides a source of the ion for many cellular signaling events. Less is known about the dynamics of other intracellular ions. The present study investigated the intracellular source of zinc (Zn2+) that has been reported to play a role in cell signaling.
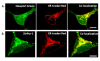
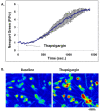
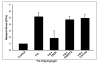
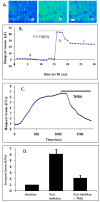
Results: In primary cultured cortical cells (neurons) labeled with intracellular fluorescent Zn2+ indicators, we showed that intracellular regions of Zn2+ staining co-localized with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The latter was identified with ER-tracker Red, a marker for ER. The colocalization was abolished upon exposure to the Zn2+ chelator TPEN, indicating that the local Zn2+ fluorescence represented free Zn2+ localized to the ER in the basal condition. Blockade of the ER Ca2+ pump by thapsigargin produced a steady increase of intracellular Zn2+. Furthermore, we determined that the thapsigargin-induced Zn2+ increase was not dependent on extracellular Ca2+ or extracellular Zn2+, suggesting that it was of intracellular origin. The applications of caged IP3 or IP3-3Kinase inhibitor (to increase available IP3) produced a significant increase in intracellular Zn2+.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results suggest that Zn2+ is sequestered into thapsigargin/IP3-sensitive stores and is released upon agonist stimulation.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

