Trafficking guidance receptors
- PMID: 20504966
- PMCID: PMC2890194
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001826
Trafficking guidance receptors
Abstract
Wiring of the brain relies initially on the correct outgrowth of axons to reach the appropriate target area for innervation. A large number of guidance receptors present in the plasma membrane of axonal growth cones and elsewhere on the neuron read and execute directional cues present in the extracellular environment of the navigating growth cone. The exact timing, levels, and localization of expression of the guidance receptors in the plasma membrane therefore determine the outcome of guidance decisions. Many guidance receptors are localized in exquisitely precise spatial and temporal patterns. The cellular mechanisms ensuring these localization patterns include spatially accurate sorting after synthesis in the secretory pathway, retrieval of inappropriately expressed receptors by endocytosis followed by degradation or recycling, and restriction of diffusion. This article will discuss the machinery and regulation underlying the restricted distribution of membrane receptors, focusing on the currently best-studied example, the L1 cell adhesion molecule. In addition to the long-range mechanisms ensuring appropriate localization, the same mechanisms can act locally to adjust levels and localization of receptors. These local mechanisms are regulated by ligand binding and subsequent activation of local signaling cascades. It is likely that the localization of all guidance receptors is regulated by a combination of sorting, retrieval, recycling and retention, similar to the ones we discuss here for L1.
Figures
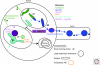
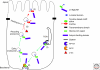

They can be directly sorted to the axon from the TGN based on sorting signals and association with axonally directed motor proteins (orange pathway: direct sorting).
They can be sorted in the TGN to the somatodendritic domain and be redirected to the axon after endocytosis (purple pathway: transcytosis).
They can be uniformly inserted into the plasma membrane in the axonal and somatodendritic domains and then be removed preferentially from the somatodendritic domain and stabilized in the axon (green pathway: domain-specific retrieval/retention).
Similar articles
-
Endocytosis and endosomes at the crossroads of regulating trafficking of axon outgrowth-modifying receptors.Traffic. 2011 Sep;12(9):1099-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01213.x. Epub 2011 May 23. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21535338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidance of Axons by Local Coupling of Retrograde Flow to Point Contact Adhesions.J Neurosci. 2016 Feb 17;36(7):2267-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2645-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26888936 Free PMC article.
-
Axon guidance receptors: Endocytosis, trafficking and downstream signaling from endosomes.Prog Neurobiol. 2021 Mar;198:101916. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101916. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32991957 Review.
-
Axonal wiring in neural development: Target-independent mechanisms help to establish precision and complexity.Bioessays. 2015 Sep;37(9):996-1004. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400222. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26184069 Review.
-
NILE/L1 and NCAM-polysialic acid expression on growing axons of isolated neurons.J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jun 8;332(2):237-57. doi: 10.1002/cne.903320208. J Comp Neurol. 1993. PMID: 8331215
Cited by
-
Endocytosis and endosomes at the crossroads of regulating trafficking of axon outgrowth-modifying receptors.Traffic. 2011 Sep;12(9):1099-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01213.x. Epub 2011 May 23. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21535338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospho-Regulation of Soma-to-Axon Transcytosis of Neurotrophin Receptors.Dev Cell. 2017 Sep 25;42(6):626-639.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28919207 Free PMC article.
-
The making of a node: a co-production of neurons and glia.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;23(6):1049-56. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23831261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinesin-1-mediated axonal transport of CB1 receptors is required for cannabinoid-dependent axonal growth and guidance.Development. 2020 Apr 20;147(8):dev184069. doi: 10.1242/dev.184069. Development. 2020. PMID: 32265198 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal acidification by Na+/H+ exchanger NHE5 regulates TrkA cell-surface targeting and NGF-induced PI3K signaling.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Nov;24(21):3435-48. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0445. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 24006492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmari SE, Buchanan J, Smith SJ 2000. Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets. Nat Neurosci 3:445–451 - PubMed
-
- Alberts P, Rudge R, Hinners I, Muzerelle A, Martinez-Arca S, Irinopoulou T, Marthiens V, Tooze S, Rathjen F, Gaspar P, et al.2003. Cross talk between tetanus neurotoxin-insensitive vesicle-associated membrane protein-mediated transport and L1-mediated adhesion. Mol Biol Cell 14:4207–4220 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen J, Chilton JK 2009. The specific targeting of guidance receptors within neurons: who directs the directors? Dev Biol 327:4–11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
