Constitutive CD40L expression on B cells prematurely terminates germinal center response and leads to augmented plasma cell production in T cell areas
- PMID: 20505142
- PMCID: PMC3708602
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901689
Constitutive CD40L expression on B cells prematurely terminates germinal center response and leads to augmented plasma cell production in T cell areas
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2010 Aug 15;185(4):2631
Abstract
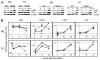
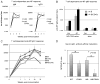
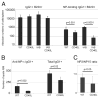
CD40/CD40L engagement is essential to T cell-dependent B cell proliferation and differentiation. However, the precise role of CD40 signaling through cognate T-B interaction in the generation of germinal center and memory B cells is still incompletely understood. To address this issue, a B cell-specific CD40L transgene (CD40LBTg) was introduced into mice with B cell-restricted MHC class II deficiency. Using this mouse model, we show that constitutive CD40L expression on B cells alone could not induce germinal center differentiation of MHC class II-deficient B cells after immunization with T cell-dependent Ag. Thus, some other MHC class II-dependent T cell-derived signals are essential for the generation of germinal center B cells in response to T cell-dependent Ag. In fact, CD40LBTg mice generated a complex Ag-specific IgG1 response, which was greatly enhanced in early, but reduced in late, primary response compared with control mice. We also found that the frequency of Ag-specific germinal center B cells in CD40LBTg mice was abruptly reduced 1 wk after immunization. As a result, the numbers of Ag-specific IgG1 long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells were reduced. By histology, large numbers of Ag-specific plasma cells were found in T cell areas adjacent to Ag-specific germinal centers of CD40LBTg mice, temporarily during the second week of primary response. These results indicate that CD40L expression on B cells prematurely terminated their ongoing germinal center response and produced plasma cells. Our results support the notion that CD40 signaling is an active termination signal for germinal center reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


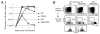

References
-
- Berberich I, Shu GL, Clark EA. Cross-linking CD40 on B cells rapidly activates nuclear factor-kappa B. J Immunol. 1994;153:4357–4366. - PubMed
-
- Kawabe T, Naka T, Yoshida K, Tanaka T, Fujiwara H, Suematsu S, Yoshida N, Kishimoto T, Kikutani H. The immune responses in CD40-deficient mice: impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1994;1:167–178. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Foy TM, Laman JD, Elliott EA, Dunn JJ, Waldschmidt TJ, Elsemore J, Noelle RJ, Flavell RA. Mice deficient for the CD40 ligand. Immunity. 1994;1:423–431. - PubMed
-
- Filion LG, Matusevicius D, Graziani-Bowering GM, Kumar A, Freedman MS. Monocyte-derived IL12, CD86 (B7-2) and CD40L expression in relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol. 2003;106:127–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

