The glutamate release inhibitor Riluzole decreases migration, invasion, and proliferation of melanoma cells
- PMID: 20505744
- PMCID: PMC4004181
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2010.126
The glutamate release inhibitor Riluzole decreases migration, invasion, and proliferation of melanoma cells
Abstract
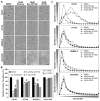
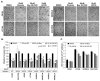
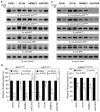
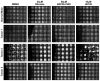
The goal of this study was to examine the effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor-1 (GRM1) blockade on melanoma anchorage-independent growth and invasion. We performed colony and invasion assays using GRM1-expressing melanoma lines and the GRM1-negative UACC930 line. Using the glutamate-release inhibitor Riluzole or the non-competitive GRM1 antagonist BAY 36-7620 we were able to induce considerable inhibition of colony formation and invasion in GRM1-expressing melanoma lines. Neither pharmacological agent induced significant reduction in colony formation or invasion in the GRM1-negative melanoma line, UACC930. Additionally we assessed the efficacy of these inhibitors to inhibit the growth of fresh melanoma tumor samples cultured on a 74-mum nylon mesh. Both Riluzole and BAY 36-7620 significantly inhibited tumor cell growth into the interstitial spaces of the mesh. When repeated with normal mole samples both inhibitors were much less effective in preventing the outgrowth of cells. These experiments show that a specific antagonist of GRM1 (BAY 36-7620) or an inhibitor of glutamate release (Riluzole) can significantly suppress melanoma migration, invasion and colony formation as well as inhibit the proliferation of fresh melanoma cells. These findings, added to our previous work, strengthen the case that GRM1 is a valid therapeutic target in patients with melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 and glutamate signaling in human melanoma.Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;67(5):2298-305. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3665. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332361
-
Concurrent Targeting of Glutaminolysis and Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 (GRM1) Reduces Glutamate Bioavailability in GRM1+ Melanoma.Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 15;79(8):1799-1809. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1500. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30987979 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic pathway targeting in melanoma: single-agent and combinatorial therapies.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 15;17(22):7080-92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0098. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21844014 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic signaling in cellular transformation.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 May;25(3):331-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.00983.x. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012. PMID: 22273393 Review.
-
From existing therapies to novel targets: a current view on melanoma.Front Biosci. 2006 Sep 1;11:2081-92. doi: 10.2741/1951. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16720295 Review.
Cited by
-
Riluzole Enhances the Response of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells to Ionizing Radiation via ATM/P53 Signalling Pathway.J Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;11(11):3089-3098. doi: 10.7150/jca.41217. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32231713 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the glutamate receptor GRM1 enhances angiogenic signaling to drive melanoma progression.Cancer Res. 2014 May 1;74(9):2499-509. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1531. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24491800 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor-1 as a novel target for the antiangiogenic treatment of breast cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 14;9(3):e88830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088830. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24633367 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of Secondary Melanoma on C57BL/6J Mouse Liver Using 1H NMR Metabolomics.Metabolites. 2013 Oct 31;3(4):1011-35. doi: 10.3390/metabo3041011. Metabolites. 2013. PMID: 24958263 Free PMC article.
-
Riluzole-induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma is mediated through Yes-associated protein upon phosphorylation by c-Abl Kinase.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 25;11(1):20974. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00439-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34697383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng GZ, Chan J, Wang Q, Zhang W, Sun CD, Wang LH. Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion, and resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1979–1987. - PubMed
-
- Chong ZZ, Kang JQ, Maiese K. Metabotropic glutamate receptors promote neuronal and vascular plasticity through novel intracellular pathways. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Dummer R, Hauschild A, Pentheroudakis G. Cutaneous malignant melanoma: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(Suppl 4):129–131. - PubMed
-
- Fagni L, Ango F, Perroy J, Bockaert J. Identification and functional roles of metabotropic glutamate receptor-interacting proteins. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

