Determination of therapeutic equivalence of generic products of gentamicin in the neutropenic mouse thigh infection model
- PMID: 20505762
- PMCID: PMC2873963
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010744
Determination of therapeutic equivalence of generic products of gentamicin in the neutropenic mouse thigh infection model
Abstract
Background: Drug regulatory agencies (DRA) support prescription of generic products of intravenous antibiotics assuming therapeutic equivalence from pharmaceutical equivalence. Recent reports of deaths associated with generic heparin and metoprolol have raised concerns about the efficacy and safety of DRA-approved drugs.
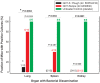
Methodology/principal findings: To challenge the assumption that pharmaceutical equivalence predicts therapeutic equivalence, we determined in vitro and in vivo the efficacy of the innovator product and 20 pharmaceutically equivalent generics of gentamicin. The data showed that, while only 1 generic product failed in vitro (MIC = 45.3 vs. 0.7 mg/L, P<0.05), 10 products (including gentamicin reference powder) failed in vivo against E. coli due to significantly inferior efficacy (E(max) = 4.81 to 5.32 vs. 5.99 log(10) CFU/g, P<or =0.043). Although the design lacked power to detect differences in survival after thigh infection with P. aeruginosa, dissemination to vital organs was significantly higher in animals treated with generic gentamicin despite 4 days of maximally effective treatment.
Conclusion: Pharmaceutical equivalence does not predict therapeutic equivalence of generic gentamicin. Stricter criteria based on solid experimental evidence should be required before approval for human use.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

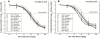

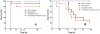
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo comparison of the anti-staphylococcal efficacy of generic products and the innovator of oxacillin.BMC Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 4;10:153. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-153. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20525378 Free PMC article.
-
Generic vancomycin products fail in vivo despite being pharmaceutical equivalents of the innovator.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Aug;54(8):3271-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01044-09. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20547818 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic equivalence requires pharmaceutical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic identities: true bioequivalence of a generic product of intravenous metronidazole.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 May;56(5):2659-65. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06012-11. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22330928 Free PMC article.
-
Potential concerns about generic substitution: bioequivalence versus therapeutic equivalence of different amlodipine salt forms.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Sep;25(9):2179-89. doi: 10.1185/03007990903116867. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19601710 Review.
-
Regulatory considerations of pharmaceutical solid polymorphism in Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDAs).Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004 Feb 23;56(3):397-414. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2003.10.011. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. PMID: 14962589 Review.
Cited by
-
Generic vancomycin enriches resistant subpopulations of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure in a neutropenic mouse thigh infection model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jan;56(1):243-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05129-11. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22064531 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of tramadol on bacterial burden in the standard neutropenic thigh infection model.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 15;12(1):19606. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24111-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36380116 Free PMC article.
-
Impact on Bacterial Resistance of Therapeutically Nonequivalent Generics: The Case of Piperacillin-Tazobactam.PLoS One. 2016 May 18;11(5):e0155806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155806. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27191163 Free PMC article.
-
An optimized mouse thigh infection model for enterococci and its impact on antimicrobial pharmacodynamics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jan;59(1):233-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02352-13. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25348523 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo comparison of the anti-staphylococcal efficacy of generic products and the innovator of oxacillin.BMC Infect Dis. 2010 Jun 4;10:153. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-153. BMC Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20525378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henry D, Lexchin J. The pharmaceutical industry as a medicines provider. Lancet. 2002;360:1590; 1–1595. S0140-6736(02)11527-3 [pii];10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11527-3 [doi] - PubMed
-
- Kirking DM, Ascione FJ, Gaither CA, Welage LS. Economics and structure of the generic pharmaceutical industry. J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash ) 2001;41:578–584. - PubMed
-
- Mastoraki E, Michalopoulos A, Kriaras I, Mouchtouri E, Falagas M, et al. Incidence of postoperative infections in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery receiving antimicrobial prophylaxis with original and generic cefuroxime. J Infect. 2008;56:35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

