Agrin binds BMP2, BMP4 and TGFbeta1
- PMID: 20505824
- PMCID: PMC2874008
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010758
Agrin binds BMP2, BMP4 and TGFbeta1
Abstract
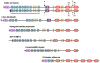
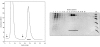
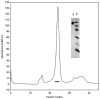
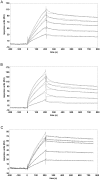
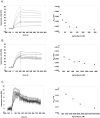
The C-terminal 95 kDa fragment of some isoforms of vertebrate agrins is sufficient to induce clustering of acetylcholine receptors but despite two decades of intense agrin research very little is known about the function of the other isoforms and the function of the larger, N-terminal part of agrins that is common to all isoforms. Since the N-terminal part of agrins contains several follistatin-domains, a domain type that is frequently implicated in binding TGFbetas, we have explored the interaction of the N-terminal part of rat agrin (Agrin-Nterm) with members of the TGFbeta family using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and reporter assays. Here we show that agrin binds BMP2, BMP4 and TGFbeta1 with relatively high affinity, the K(D) values of the interactions calculated from SPR experiments fall in the 10(-8) M-10(-7) M range. In reporter assays Agrin-Nterm inhibited the activities of BMP2 and BMP4, half maximal inhibition being achieved at approximately 5x10(-7) M. Paradoxically, in the case of TGFbeta1 Agrin N-term caused a slight increase in activity in reporter assays. Our finding that agrin binds members of the TGFbeta family may have important implications for the role of these growth factors in the regulation of synaptogenesis as well as for the role of agrin isoforms that are unable to induce clustering of acetylcholine receptors. We suggest that binding of these TGFbeta family members to agrin may have a dual function: agrin may serve as a reservoir for these growth factors and may also inhibit their growth promoting activity. Based on analysis of the evolutionary history of agrin we suggest that agrin's growth factor binding function is more ancient than its involvement in acetylcholine receptor clustering.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
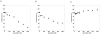
Similar articles
-
WFIKKN1 and WFIKKN2 bind growth factors TGFβ1, BMP2 and BMP4 but do not inhibit their signalling activity.FEBS J. 2010 Dec;277(24):5040-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07909.x. Epub 2010 Nov 5. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 21054789
-
A neuronal inhibitory domain in the N-terminal half of agrin.J Neurobiol. 2002 Feb 5;50(2):164-79. doi: 10.1002/neu.10025. J Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11793362
-
Agrin binding to alpha-dystroglycan. Domains of agrin necessary to induce acetylcholine receptor clustering are overlapping but not identical to the alpha-dystroglycan-binding region.J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):5231-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.5231. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8617807
-
Functions of agrin and agrin-related proteins.Trends Neurosci. 1993 Feb;16(2):76-81. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90021-d. Trends Neurosci. 1993. PMID: 7680504 Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Endogenous Tagging of Basement Membrane Components Reveals Dynamic Movement within the Matrix Scaffolding.Dev Cell. 2020 Jul 6;54(1):60-74.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.05.022. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 32585132 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 6 as a putative risk factor in neuromuscular degeneration.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089183. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586579 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Role of the Extracellular Matrix Within the Liver Disease Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 11;11:574276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574276. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33262757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MuSK-BMP pathway regulates synaptic Nav1.4 localization and muscle excitability.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 29:2023.10.24.563837. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.24.563837. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37961580 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Thrombospondins as key regulators of synaptogenesis in the central nervous system.Matrix Biol. 2012 Apr;31(3):170-7. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2012.01.004. Epub 2012 Jan 21. Matrix Biol. 2012. PMID: 22285841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bezakova G, Rüegg MA. New insights into the roles of agrin. Nature Rev Molec Cell Biol. 2003;4:295–308. - PubMed
-
- Kummer TT, Misgeld T, Sanes JR. Assembly of the postsynaptic membrane at the neuromuscular junction: paradigm lost. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16:74–82. - PubMed
-
- Annies M, Bittcher G, Ramseger R, Loschinger J, Woll S, et al. Clustering transmembrane-agrin induces filopodia-like processes on axons and dendrites. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;31:515–524. - PubMed
-
- McCroskery S, Chaudhry A, Lin L, Daniels MP. Transmembrane agrin regulates filopodia in rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006;33:15–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

