Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of radiation-induced macular ischemia
- PMID: 20505835
- PMCID: PMC2874270
- DOI: 10.2147/opth.s9803
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of radiation-induced macular ischemia
Abstract
Purpose: To report a case of radiation-induced macular ischemia where vision and macular perfusion improved after hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy.
Methods: A 62-year-old male patient developed radiation-induced macular ischemia after he was treated with radiation for brain glioma. The patient presented with best spectacle-corrected visual acuity (BSCVA) acuity of 20/400 in his right eye. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed central macular thickness of 468 mum. The patient received focal laser, intravitreal triamcinolone, and HBO therapy.
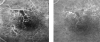
Results: The patient's vision improved from 20/400 to 20/100 after focal laser and intravitreal triamcinolone. His central macular thickness improved from 468 mum to 132 mum. After receiving HBO therapy, his VA improved to 20/50 and fluorescein angiography showed improvement in macular perfusion.
Conclusion: HBO therapy improves macular perfusion in patients with radiation-induced macular ischemia.
Keywords: hyperbaric oxygen therapy; macular ischemia; macular perfusion; visual acuity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term effect of intravitreal bevacizumab (avastin) in patients with chronic diffuse diabetic macular edema.Retina. 2008 Oct;28(8):1053-60. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e318176de48. Retina. 2008. PMID: 18779710
-
POSSIBLE EFFICACY OF TOPICAL DORZOLAMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF PACLITAXEL-RELATED CYSTOID MACULAR EDEMA.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018 Winter;12(1):75-79. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000433. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2018. PMID: 27749791
-
Combined treatment with intravitreal bevacizumab and laser photocoagulation for exudative maculopathy in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.Ophthalmic Genet. 2017 Sep-Oct;38(5):490-493. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2017.1279183. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Ophthalmic Genet. 2017. PMID: 28121209
-
Prospective study of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide versus bevacizumab for macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion.Retina. 2011 May;31(5):838-45. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181f4420d. Retina. 2011. PMID: 21293319 Clinical Trial.
-
Practical Lessons from Protocol I for the Management of Diabetic Macular Edema.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;60:91-108. doi: 10.1159/000459692. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28427069 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as rescue therapy for pediatric frosted branch angiitis with Purtscher-like retinopathy: A case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 17;10:1119623. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1119623. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37138735 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Changes in Diabetic Macular Ischemia after Systemic Normobaric Oxygen Therapy.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2025 May 19;20:10.18502/jovr.v20.15354. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v20.15354. eCollection 2025. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2025. PMID: 40689112 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic oxygen therapy versus oral enalapril for treatment of diabetic macular ischemia: a randomized controlled trial.Int Ophthalmol. 2016 Apr;36(2):225-35. doi: 10.1007/s10792-015-0123-1. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Int Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26292645 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of hyperbaric oxygen in glioma: a narrative review.Med Gas Res. 2022 Jan-Mar;12(1):1-5. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.324589. Med Gas Res. 2022. PMID: 34472495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stallard HB. Radiation energy as (a) a pathogenic (b) a therapeutic agent in ophthalmic disorders. Br J Ophthalmol. 1933;1:70.
-
- Kinyoun JL, Chittum ME, Wells CG. Photocoagulation treatment of radiation retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988;105:470–478. - PubMed
-
- Sutter FK, Gillies MC. Intravitreal triamcinolone for radiation-induced macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121(10):1491–1493. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A, Muecke JS. Treatment of radiation maculopathy with intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (Avastin) Retina. 2008;28(7):964–968. - PubMed
-
- Oguz H, Sobaci G. The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in ophthalmology. Surv Ophthalmol. 2008;53(2):112–120. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

