Prevention of cartilage degeneration and restoration of chondroprotection by lubricin tribosupplementation in the rat following anterior cruciate ligament transection
- PMID: 20506144
- PMCID: PMC2921027
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27550
Prevention of cartilage degeneration and restoration of chondroprotection by lubricin tribosupplementation in the rat following anterior cruciate ligament transection
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether cartilage degeneration is prevented or minimized following intraarticular injections of lubricin derived from human synoviocytes in culture, recombinant human PRG4 (rhPRG4), or human synovial fluid (SF) in a rat model of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury.
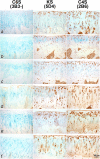
Methods: Unilateral ACL transection (ACLT) was performed in Lewis rats (n = 45). Nine animals were left untreated. The remaining rats were given intraarticular injections (50 microl/injection) of either phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (n = 9), human synoviocyte lubricin (200 microg/ml; n = 9), rhPRG4 (200 microg/ml; n = 9), or human SF lubricin (200 microg/ml; n = 9) twice weekly beginning on day 7 after injury. Joints were harvested on day 32 after injury. Histologic analysis was performed using Safranin O-fast green staining, and articular cartilage degeneration was graded using the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI)-modified Mankin criteria. Histologic specimens were immunoprobed for lubricin and sulfated glycosaminoglycans. A 24-hour urine collection was performed on days 17 and 29 postinjury, and urinary C-terminal telopeptide of type II collagen (CTX-II) levels were measured.
Results: Treatment with human synoviocyte lubricin resulted in significantly lower OARSI scores for cartilage degeneration compared with no treatment or PBS treatment (P < 0.05). Increased immunostaining for lubricin in the superficial zone chondrocytes and on the surface of cartilage was observed in lubricin-treated, but not untreated or PBS-treated, joints. On day 17, urinary CTX-II levels in human synoviocyte lubricin- and human SF lubricin-treated animals were significantly lower than those in untreated animals (P = 0.005 and P = 0.002, respectively) and in PBS-treated animals (P = 0.002 and P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: After treatment with any of the 3 types of lubricin evaluated in this study, a reduction in cartilage damage following ACLT was evident, combined with a reduction in type II collagen degradation. Our findings indicate that intraarticular lubricin injection following an ACL injury may be beneficial in retarding the degeneration of cartilage and the development of posttraumatic OA.
Figures




References
-
- Aichroth PM, Patel DV, Zorrilla P. The natural history and treatment of rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament in children and adolescents. A prospective review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(1):38–41. - PubMed
-
- Fithian DC, Paxton LW, Goltz DH. Fate of the anterior cruciate ligament-injured knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002;33(4):621–36. v. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Moses JM, Papannagari R, Pathare NP, DeFrate LE, Gill TJ. Anterior cruciate ligament deficiency alters the in vivo motion of the tibiofemoral cartilage contact points in both the anteroposterior and mediolateral directions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1826–34. - PubMed
-
- Roos H, Adalberth T, Dahlberg L, Lohmander LS. Osteoarthritis of the knee after injury to the anterior cruciate ligament or meniscus: the influence of time and age. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1995;3(4):261–7. - PubMed
-
- Vasara AI, Jurvelin JS, Peterson L, Kiviranta I. Arthroscopic cartilage indentation and cartilage lesions of anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knees. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(3):408–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

