Cellular and subcellular localization of estrogen and progestin receptor immunoreactivities in the mouse hippocampus
- PMID: 20506473
- PMCID: PMC2879091
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22361
Cellular and subcellular localization of estrogen and progestin receptor immunoreactivities in the mouse hippocampus
Abstract
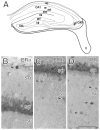
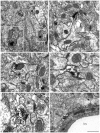
Estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha), estrogen receptor-beta (ERbeta), and progestin receptor (PR) immunoreactivities are localized to extranuclear sites in the rat hippocampal formation. Because rats and mice respond differently to estradiol treatment at a cellular level, the present study examined the distribution of ovarian hormone receptors in the dorsal hippocampal formation of mice. For this, antibodies to ERalpha, ERbeta, and PR were localized by light and electron immunomicroscopy in male and female mice across the estrous cycle. Light microscopic examination of the mouse hippocampal formation showed sparse nuclear ERalpha and PR immunoreactivity (-ir) most prominently in the CA1 region and diffuse ERbeta-ir primarily in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer as well as in a few interneurons. Ultrastructural analysis additionally revealed discrete extranuclear ERalpha-, ERbeta-, and PR-ir in neuronal and glial profiles throughout the hippocampal formation. Although extranuclear profiles were detected in all animal groups examined, the amount and types of profiles varied with sex and estrous cycle phase. ERalpha-ir was highest in diestrus females, particularly in dendritic spines, axons, and glia. Similarly, ERbeta-ir was highest in estrus and diestrus females, mainly in dendritic spines and glia. Conversely, PR-ir was highest during proestrus, mostly in axons. Except for very low levels of extranuclear ERbeta-ir in mossy fiber terminals in mice, the labeling patterns in the mice for all three antibodies were similar to the ultrastructural labeling found previously in rats, suggesting that regulation of these receptors is well conserved across the two species.
Figures



References
-
- Alves SE, McEwen BS, Hayashi S, Korach KS, Pfaff DW, Ogawa S. Estrogen-regulated progestin receptors are found in the midbrain raphe but not hippocampus of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) gene-disrupted mice. J Comp Neurol. 2000;427:185–195. - PubMed
-
- Alves SE, Weiland NG, Hayashi S, McEwen BS. Immunocytochemical localization of nuclear estrogen receptors and progestin receptors within the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1998;391:322–334. - PubMed
-
- Arias C, Zepeda A, Hernandez-Ortega K, Leal-Galicia P, Lojero C, Camacho-Arroyo I. Sex and estrous cycle-dependent differences in glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the adult rat hippocampus. Horm Behav. 2009;55:257–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

