Synergistic effects of tea polyphenols and ascorbic acid on human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells
- PMID: 20506578
- PMCID: PMC2880360
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0900355
Synergistic effects of tea polyphenols and ascorbic acid on human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells
Abstract
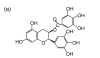
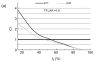
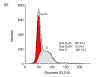
Tea polyphenols have been shown to have anticancer activity in many studies. In the present study, we investigated effects of theaflavin-3-3'-digallate (TF(3)), one of the major theaflavin monomers in black tea, in combination with ascorbic acid (AA), a reducing agent, and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the main polyphenol presented in green tea, in combination with AA on cellular viability and cell cycles of the human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay showed that the 50% inhibition concentrations (IC(50)) of TF(3), EGCG, and AA on SPC-A-1 cells were 4.78, 4.90, and 30.62 micromol/L, respectively. The inhibitory rates of TF(3) combined with AA (TF(3)+AA) and EGCG combined with AA (EGCG+AA) at a molar ratio of 1:6 on SPC-A-1 cells were 54.4% and 45.5%, respectively. Flow cytometry analysis showed that TF(3)+AA and EGCG+AA obviously increased the cell population in the G(0)/G(1) phase of the SPC-A-1 cell cycle from 53.9% to 62.8% and 60.0%, respectively. TF(3)-treated cells exhibited 65.3% of the G(0)/G(1) phase at the concentration of its IC(50). Therefore, TF(3)+AA and EGCG+AA had synergistic inhibition effects on the proliferation of SPC-A-1 cells, and significantly held SPC-A-1 cells in G(0)/G(1) phase. The results suggest that the combination of TF(3) with AA or EGCG with AA enhances their anticancer activity.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Enhancement of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and theaflavin-3-3'-digallate induced apoptosis by ascorbic acid in human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells and esophageal carcinoma Eca-109 cells via MAPK pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Aug 23;438(2):370-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.078. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23892041
-
Suppression of extracellular signals and cell proliferation by the black tea polyphenol, theaflavin-3,3'-digallate.Carcinogenesis. 1999 Apr;20(4):733-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.4.733. Carcinogenesis. 1999. PMID: 10223207
-
Effect of black and green tea polyphenols on c-jun phosphorylation and H(2)O(2) production in transformed and non-transformed human bronchial cell lines: possible mechanisms of cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction.Carcinogenesis. 2000 Nov;21(11):2035-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.11.2035. Carcinogenesis. 2000. PMID: 11062165
-
Cancer chemoprevention by tea polyphenols through modulating signal transduction pathways.Arch Pharm Res. 2002 Oct;25(5):561-71. doi: 10.1007/BF02976924. Arch Pharm Res. 2002. PMID: 12433185 Review.
-
Cancer chemoprevention by tea polyphenols through mitotic signal transduction blockade.Biochem Pharmacol. 1999 Sep 15;58(6):911-5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00112-4. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10509743 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ascorbic Acid.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 7;11(10):1993. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101993. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic effect of black tea polyphenol, theaflavin-3,3'-digallate with cisplatin against cisplatin resistant human ovarian cancer cells.J Funct Foods. 2018 Jul;46:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.04.037. Epub 2018 Apr 26. J Funct Foods. 2018. PMID: 30364631 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of four main theaflavin derivatives through chemiluminescence and DNA damage analyses.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011 Sep;12(9):744-51. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1100041. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011. PMID: 21887850 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea polyphenols and their potential role in health and disease.Inflammopharmacology. 2015 Aug;23(4):151-61. doi: 10.1007/s10787-015-0236-1. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Inflammopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26164000 Review.
-
The Inhibitory Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Viability of T Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells is Associated with Increase of Caspase-3 Level and Fas Expression.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2018 Apr;34(2):253-260. doi: 10.1007/s12288-017-0854-4. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2018. PMID: 29622866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal R, Mukhtar H. Cancer chemoprevention by polyphenols in green tea and artichoke. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1996;401:35–50. - PubMed
-
- Chung JY, Huang CS, Meng XF, Yang CS. Inhibition of activator protein 1 activity and cell growth by purified green tea and black tea polyphenols in H-ras-transformed cells: structure-activity relationship and mechanisms involved. Cancer Research. 1999;59(18):4610–4617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

