Obesity and cancer
- PMID: 20507889
- PMCID: PMC3227989
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0285
Obesity and cancer
Abstract
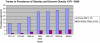
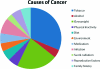
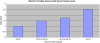
Weight, weight gain, and obesity account for approximately 20% of all cancer cases. Evidence on the relation of each to cancer is summarized, including esophageal, thyroid, colon, renal, liver, melanoma, multiple myeloma, rectum, gallbladder, leukemia, lymphoma, and prostate in men; and postmenopausal breast and endometrium in women. Different mechanisms drive etiologic pathways for these cancers. Weight loss, particularly among postmenopausal women, reduces risk for breast cancer. Among cancer patients, data are less robust, but we note a long history of poor outcomes after breast cancer among obese women. While evidence on obesity and outcomes for other cancers is mixed, growing evidence points to benefits of physical activity for breast and colon cancers. Dosing of chemotherapy and radiation therapy among obese patients is discussed and the impact on therapy-related toxicity is noted. Guidelines for counseling patients for weight loss and increased physical activity are presented and supported by strong evidence that increased physical activity leads to improved quality of life among cancer survivors. The "Five A's" model guides clinicians through a counseling session: assess, advise, agree, assist, arrange. The burden of obesity on society continues to increase and warrants closer attention by clinicians for both cancer prevention and improved outcomes after diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The content of this article has been reviewed by independent peer reviewers to ensure that it is balanced, objective, and free from commercial bias. No financial relationships relevant to the content of this article have been disclosed by the authors or independent peer reviewers.
Figures


References
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625–1638. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002;288:1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Weight Control and Physical Activity. Volume 6. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2002. pp. 1–315.
-
- Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, et al. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet. 2008;371:569–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

