iPARTS: an improved tool of pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures
- PMID: 20507908
- PMCID: PMC2896121
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq483
iPARTS: an improved tool of pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures
Abstract
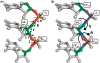
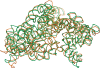
iPARTS is an improved web server for aligning two RNA 3D structures based on a structural alphabet (SA)-based approach. In particular, we first derive a Ramachandran-like diagram of RNAs by plotting nucleotides on a 2D axis using their two pseudo-torsion angles eta and . Next, we apply the affinity propagation clustering algorithm to this eta- plot to obtain an SA of 23-nt conformations. We finally use this SA to transform RNA 3D structures into 1D sequences of SA letters and continue to utilize classical sequence alignment methods to compare these 1D SA-encoded sequences and determine their structural similarities. iPARTS takes as input two RNA 3D structures in the PDB format and outputs their global alignment (for determining overall structural similarity), semiglobal alignments (for detecting structural motifs or substructures), local alignments (for finding locally similar substructures) and normalized local structural alignments (for identifying more similar local substructures without non-similar internal fragments), with graphical display that allows the user to visually view, rotate and enlarge the superposition of aligned RNA 3D structures. iPARTS is now available online at http://bioalgorithm.life.nctu.edu.tw/iPARTS/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SARSA: a web tool for structural alignment of RNA using a structural alphabet.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul 1;36(Web Server issue):W19-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn327. Epub 2008 May 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18502774 Free PMC article.
-
iPARTS2: an improved tool for pairwise alignment of RNA tertiary structures, version 2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W328-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw412. Epub 2016 May 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27185896 Free PMC article.
-
DIAL: a web server for the pairwise alignment of two RNA three-dimensional structures using nucleotide, dihedral angle and base-pairing similarities.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W659-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm334. Epub 2007 Jun 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567620 Free PMC article.
-
R3D-BLAST2: an improved search tool for similar RNA 3D substructures.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Dec 28;18(Suppl 16):574. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1956-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29297283 Free PMC article.
-
R3D-BLAST: a search tool for similar RNA 3D substructures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(Web Server issue):W45-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr379. Epub 2011 May 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21624889 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RMalign: an RNA structural alignment tool based on a novel scoring function RMscore.BMC Genomics. 2019 Apr 8;20(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5631-3. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30961545 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive survey of long-range tertiary interactions and motifs in non-coding RNA structures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Sep 8;51(16):8367-8382. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad605. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37471030 Free PMC article.
-
SARA-Coffee web server, a tool for the computation of RNA sequence and structure multiple alignments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(Web Server issue):W356-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku459. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24972831 Free PMC article.
-
A new way to see RNA.Q Rev Biophys. 2011 Nov;44(4):433-66. doi: 10.1017/S0033583511000059. Epub 2011 May 18. Q Rev Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21729350 Free PMC article.
-
CircularSTAR3D: a stack-based RNA 3D structural alignment tool for circular matching.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 May 22;51(9):e53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad222. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36987885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dror O, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ. ARTS: alignment of RNA tertiary structures. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:47–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

