Protein annotation and modelling servers at University College London
- PMID: 20507913
- PMCID: PMC2896093
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq427
Protein annotation and modelling servers at University College London
Abstract
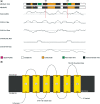
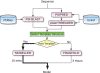
The UCL Bioinformatics Group web portal offers several high quality protein structure prediction and function annotation algorithms including PSIPRED, pGenTHREADER, pDomTHREADER, MEMSAT, MetSite, DISOPRED2, DomPred and FFPred for the prediction of secondary structure, protein fold, protein structural domain, transmembrane helix topology, metal binding sites, regions of protein disorder, protein domain boundaries and protein function, respectively. We also now offer a fully automated 3D modelling pipeline: BioSerf, which performed well in CASP8 and uses a fragment-assembly approach which placed it in the top five servers in the de novo modelling category. The servers are available via the group web site at http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/.
Figures

References
-
- Jones DT. Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;292:195–202. - PubMed
-
- Jones DT. Improving the accuracy of transmembrane protein topology prediction using evolutionary information. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:538–544. - PubMed
-
- Ward JJ, McGuffin LJ, Bryson K, Buxton BF, Jones DT. The DISOPRED server for the prediction of protein disorder. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:2138–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

