YLoc--an interpretable web server for predicting subcellular localization
- PMID: 20507917
- PMCID: PMC2896088
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq477
YLoc--an interpretable web server for predicting subcellular localization
Abstract
Predicting subcellular localization has become a valuable alternative to time-consuming experimental methods. Major drawbacks of many of these predictors is their lack of interpretability and the fact that they do not provide an estimate of the confidence of an individual prediction. We present YLoc, an interpretable web server for predicting subcellular localization. YLoc uses natural language to explain why a prediction was made and which biological property of the protein was mainly responsible for it. In addition, YLoc estimates the reliability of its own predictions. YLoc can, thus, assist in understanding protein localization and in location engineering of proteins. The YLoc web server is available online at www.multiloc.org/YLoc.
Figures
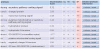
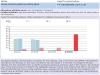
References
-
- Horton P, Nakai K. Better prediction of protein cellular localization sites with the k nearest neighbor classifier. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1997;5:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Chou K, Cai Y. Prediction and classification of protein subcellular location-sequence-order effect and pseudo amino acid composition. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003;90:1250–1260. - PubMed
-
- Nair R, Rost B. Mimicking cellular sorting improves prediction of subcellular localization. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;348:85–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

