Signatures of RNA binding proteins globally coupled to effective microRNA target sites
- PMID: 20508147
- PMCID: PMC2909566
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.103259.109
Signatures of RNA binding proteins globally coupled to effective microRNA target sites
Abstract
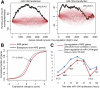
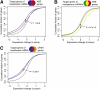
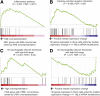
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), bound to Argonaute proteins (RISC), destabilize mRNAs through base-pairing with the mRNA. However, the gene expression changes after perturbations of these small RNAs are only partially explained by predicted miRNA/siRNA targeting. Targeting may be modulated by other mRNA sequence elements such as binding sites for the hundreds of RNA binding proteins (RNA-BPs) expressed in any cell, and this aspect has not been systematically explored. Across a panel of published experiments, we systematically investigated to what extent sequence motifs in 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) correlate with expression changes following transfection of small RNAs. The most significantly overrepresented motifs in down-regulated mRNAs are two novel U-rich motifs (URMs), UUUUAAA and UUUGUUU, recently discovered as binding sites for the ELAVL4 (also known as HuD) RNA-BP. Surprisingly, the most significantly overrepresented motif in up-regulated mRNAs is the heptanucleotide AU-rich element (ARE), UAUUUAU, which is known to affect mRNA stability via at least 20 different RNA-BPs. We show that destabilization mediated by the transfected miRNA is generally attenuated by ARE motifs and augmented by URM motifs. These ARE and URM signatures were confirmed in different types of published experiments covering eight different cell lines. Finally, we show that both ARE and URM motifs couple to presumed endogenous miRNA binding sites in mRNAs bound by Argonaute proteins. This is the first systematic investigation of 3' UTR motifs that globally couple to regulation by miRNAs and may potentially antagonize or cooperate with miRNA/siRNA regulation. Our results suggest that binding sites of miRNAs and RNA-BPs should be considered in combination when interpreting and predicting miRNA regulation in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Aznarez I, Barash Y, Shai O, He D, Zielenski J, Tsui LC, Parkinson J, Frey BJ, Rommens JM, Blencowe BJ 2008. A systematic analysis of intronic sequences downstream of 5′ splice sites reveals a widespread role for U-rich motifs and TIA1/TIAL1 proteins in alternative splicing regulation. Genome Res 18: 1247–1258 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W 2006. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell 125: 1111–1124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
