Real-Time hypoglycemia prediction suite using continuous glucose monitoring: a safety net for the artificial pancreas
- PMID: 20508231
- PMCID: PMC2875433
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1487
Real-Time hypoglycemia prediction suite using continuous glucose monitoring: a safety net for the artificial pancreas
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to develop an advanced algorithm that detects pending hypoglycemia and then suspends basal insulin delivery. This approach can provide a solution to the problem of nocturnal hypoglycemia, a major concern of patients with diabetes.
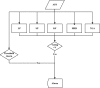
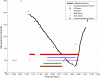
Research design and methods: This real-time hypoglycemia prediction algorithm (HPA) combines five individual algorithms, all based on continuous glucose monitoring 1-min data. A predictive alarm is issued by a voting algorithm when a hypoglycemic event is predicted to occur in the next 35 min. The HPA system was developed using data derived from 21 Navigator studies that assessed Navigator function over 24 h in children with type 1 diabetes. We confirmed the function of the HPA using a separate dataset from 22 admissions of type 1 diabetic subjects. During these admissions, hypoglycemia was induced by gradual increases in the basal insulin infusion rate up to 180% from the subject's own baseline infusion rate. RESULTS Using a prediction horizon of 35 min, a glucose threshold of 80 mg/dl, and a voting threshold of three of five algorithms to predict hypoglycemia (defined as a FreeStyle plasma glucose readings <60 mg/dl), the HPA predicted 91% of the hypoglycemic events. When four of five algorithms were required to be positive, then 82% of the events were predicted.
Conclusions: The HPA will enable automated insulin-pump suspension in response to a pending event that has been detected prior to severe immediate complications.
Figures

References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Epidemiology of severe hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Am J Med 1991;90:450–459 - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. J Pediatr 1994;125:177–188 - PubMed
-
- Raju B, Arbelaez AM, Breckenridge SM, Cryer PE: Nocturnal hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: an assessment of preventive bedtime treatments. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:2087–2092 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

