Role of heme oxygenase in inflammation, insulin-signalling, diabetes and obesity
- PMID: 20508722
- PMCID: PMC2872759
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/359732
Role of heme oxygenase in inflammation, insulin-signalling, diabetes and obesity
Abstract
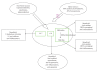
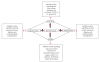
Diabetes and obesity are chronic conditions associated with elevated oxidative/inflammatory activities with a continuum of tissue insults leading to more severe cardiometabolic and renal complications including myocardial infarction and end-stage-renal damage. A common denominator of these chronic conditions is the enhanced the levels of cytokines like tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin (IL-6), IL-1beta and resistin, which in turn activates the c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) and NF-kappaB pathways, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates insulin resistance, type-2 diabetes and related complications. Emerging evidence indicates that heme oxygenase (HO) inducers are endowed with potent anti-diabetic and insulin sensitizing effects besides their ability to suppress immune/inflammatory response. Importantly, the HO system abates inflammation through several mechanisms including the suppression of macrophage-infiltration and abrogation of oxidative/inflammatory transcription factors like NF-kappaB, JNK and activating protein-1. This review highlights the mechanisms by which the HO system potentiates insulin signalling, with particular emphasis on HO-mediated suppression of oxidative and inflammatory insults. The HO system could be explored in the search for novel remedies against cardiometabolic diseases and their complications.
Figures
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, et al. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2130–2135. - PubMed
-
- McCredie M. Geographic, ethnic, age-related and temporal variation in the incidence of end-stage renal disease in Europe, Canada and the Asia-Pacific region, 1998–2002. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2006;21(8):2178–2183. - PubMed
-
- Millar WJ, Young TK. Tracking diabetes: prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Health Reports. 2003;14(3):35–47. - PubMed
-
- Bleich S, Cutler D, Murray C, Adams A. Why is the developed world obese? Annual Review of Public Health. 2008;29:273–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

