Increased carotid IMT in overweight and obese women affected by Hashimoto's thyroiditis: an adiposity and autoimmune linkage?
- PMID: 20509904
- PMCID: PMC2885992
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2261-10-22
Increased carotid IMT in overweight and obese women affected by Hashimoto's thyroiditis: an adiposity and autoimmune linkage?
Abstract
Background: Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most important cause of hypothyroidism. It is a systemic disease that can even affect the cardiovascular system, by accelerating the atherosclerotic process. Aim of this study was to examine whether autoimmune thyroiditis has an effect on the intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery (IMT-CCT), independently of the thyroid function and well-known cardiovascular risk factors. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a systemic disease. The aim is to examine whether autoimmune thyroiditis and adiposity can effect carotid IMT independently of thyroid hormones and cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: A total of 104 obese women (BMI > or = 25.0 kg/m-2), with FT3 and FT4 serum levels in the normal range and TSH levels < 4.5 microU/ml, were investigated. None of these patients was taking any kind of drug influencing thyroid function. Measurements were made of the IMT-CCT, BMI, waist circumference, blood pressure levels, as well as fasting TSH, FT3, FT4, anti-thyroid antibodies, insulin, fasting glycemia, triglycerides, total and HDL-cholesterol serum concentrations.
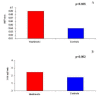
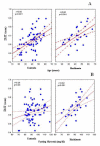
Results: Of the 104 women, 30 (28.8%) were affected by autoimmune thyroiditis. Significantly higher values of IMT-CCT (p < 0.05), TSH (p < 0.05), and triglycerides (p < 0.05) were obtained, and significantly lower values of FT4 (p < 0.05), in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis as compared to those with a normal thyroid function. When examining the whole group together, at multiple regression analysis Hashimoto's thyroiditis maintained a positive association with the IMT (p < 0.001), independently of age, hypertension, BMI, and the fasting serum levels of TSH, FT3, FT4, insulin, fasting glycemia, triglycerides, total and HDL-cholesterol levels.
Conclusions: The present study shows that Hashimoto's thyroiditis is associated to an increased IMT only in overweight and obese, independently of the thyroid function, BMI and cardiovascular risk factors. These results suggest that Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a marker of evolution of the atherosclerosis if combined to adiposity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arterial stiffness but not intima-media thickness is increased in euthyroid patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis: The effect of menopausal status.Thyroid. 2009 Aug;19(8):857-62. doi: 10.1089/thy.2008.0326. Thyroid. 2009. PMID: 19348585
-
Childhood obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors and carotid intima-media thickness.Turk J Pediatr. 2010 Nov-Dec;52(6):602-11. Turk J Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 21428192
-
Plasma leptin is independently associated with the intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001 Jun;25(6):805-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801623. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001. PMID: 11439293
-
Hashimoto's thyroiditis: An update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Oct;19(10):102649. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102649. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 32805423 Review.
-
Audiological evaluation (128-20,000Hz) in women with autoimmune thyroiditis: The role of antibodies vs. l-thyroxine deficiency.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp (Engl Ed). 2023 Jan-Feb;74(1):50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.otoeng.2021.11.005. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp (Engl Ed). 2023. PMID: 36709799 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Subclinical Hypothyroidism or Thyroid Autoimmunity on Coronary Vasospasm in Patients without Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors.Korean Circ J. 2015 Mar;45(2):125-30. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.2.125. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Korean Circ J. 2015. PMID: 25810734 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Risk in Women With PCOS.Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Fall;10(4):611-8. doi: 10.5812/ijem.4020. Epub 2012 Sep 30. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 23843832 Free PMC article.
-
THE ASSOCIATION OF SUBCLINICAL INSULIN RESISTANCE WITH THYROID AUTOIMMUNITY IN EUTHYROID INDIVIDUALS.Acta Clin Croat. 2020 Dec;59(4):696-702. doi: 10.20471/acc.2020.59.04.16. Acta Clin Croat. 2020. PMID: 34285440 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Biventricular Function in Patients with Euthyroid Hashimoto's Thyroiditis.Med Princ Pract. 2016;25(2):143-9. doi: 10.1159/000442709. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Med Princ Pract. 2016. PMID: 26613523 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Thyroid Hormone Levels and Macrovascular Complications in Euthyroid Type 2 Diabetic Patients.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 Jun 15;14:2683-2691. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S313803. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34163196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ripoli A, Pingitore A, Favilli B, Bottoni A, Turchi S, Osman NF, De Marchi D, Lombardi M, L'Abbate A, Iervasi G. Does Subclinical Hypothyroidism Affect Cardiac Pump Performance? Evidence From a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2005. pp. 439–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

