Combinatorial gene therapy renders increased survival in cirrhotic rats
- PMID: 20509929
- PMCID: PMC2890657
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-42
Combinatorial gene therapy renders increased survival in cirrhotic rats
Abstract
Background: Liver fibrosis ranks as the second cause of death in México's productive-age population. This pathology is characterized by accumulation of fibrillar proteins in hepatic parenchyma causing synthetic and metabolic disfunction. Remotion of excessive fibrous proteins might result in benefit for subjects increasing survival index. The goal of this work was to find whether the already known therapeutical effect of human urokinase Plasminogen Activator and human Matrix Metalloprotease 8 extends survival index in cirrhotic animals.
Methods: Wistar rats (80 g) underwent chronic intoxication with CCl4: mineral oil for 8 weeks. Cirrhotic animals were injected with a combined dose of Ad-delta-huPA plus Ad-MMP8 (3 x 10(11) and 1.5 x 10(11) vp/Kg, respectively) or with Ad-beta-Gal (4.5 x 10(11)) and were killed after 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 days. Then, liver and serum were collected. An additional set of cirrhotic animals injected with combined gene therapy was also monitored for their probability of survival.
Results: Only the cirrhotic animals treated with therapeutical genes (Ad-delta-huPA+Ad-MMP-8) showed improvement in liver fibrosis. These results correlated with hydroxyproline determinations. A significant decrement in alpha-SMA and TGF-beta1 gene expression was also observed. Cirrhotic rats treated with Ad-delta-huPA plus Ad-MMP8 had a higher probability of survival at 60 days with respect to Ad-beta-Gal-injected animals.
Conclusion: A single administration of Ad-delta-huPA plus Ad-MMP-8 is efficient to induce fibrosis regression and increase survival in experimental liver fibrosis.
Figures
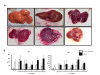



References
-
- Sistema Nacional de Información en Salud - Mortalidad. http://sinais.salud.gob.mx/mortalidad/ Accessed 28 May 2010.
-
- Rodríguez Hernández H, Jacobo Karam JS. Supervivencia de pacientes con cirrosis hepática en el Hospital General Regional del IMSS, Durango. Gaceta Medica de México. 2002;138:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

