WriteSim TCExam--an open source text simulation environment for training novice researchers in scientific writing
- PMID: 20509946
- PMCID: PMC2893514
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-10-39
WriteSim TCExam--an open source text simulation environment for training novice researchers in scientific writing
Abstract
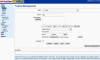
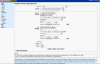
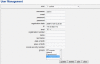
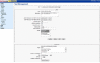
Background: The ability to write clearly and effectively is of central importance to the scientific enterprise. Encouraged by the success of simulation environments in other biomedical sciences, we developed WriteSim TCExam, an open-source, Web-based, textual simulation environment for teaching effective writing techniques to novice researchers. We shortlisted and modified an existing open source application - TCExam to serve as a textual simulation environment. After testing usability internally in our team, we conducted formal field usability studies with novice researchers. These were followed by formal surveys with researchers fitting the role of administrators and users (novice researchers)
Results: The development process was guided by feedback from usability tests within our research team. Online surveys and formal studies, involving members of the Research on Research group and selected novice researchers, show that the application is user-friendly. Additionally it has been used to train 25 novice researchers in scientific writing to date and has generated encouraging results.
Conclusion: WriteSim TCExam is the first Web-based, open-source textual simulation environment designed to complement traditional scientific writing instruction. While initial reviews by students and educators have been positive, a formal study is needed to measure its benefits in comparison to standard instructional methods.
Figures


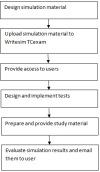
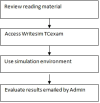
Similar articles
-
Manuscript Architect: a Web application for scientific writing in virtual interdisciplinary groups.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2005 Jun 16;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-5-15. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2005. PMID: 15960855 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific writing of novice researchers: what difficulties and encouragements do they encounter?Acad Med. 2009 Apr;84(4):511-6. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31819a8c3c. Acad Med. 2009. PMID: 19318791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of a remotely delivered, writing for publication program on publication outcomes of novice researchers.Rural Remote Health. 2018 May;18(2):4468. doi: 10.22605/RRH4468. Epub 2018 May 24. Rural Remote Health. 2018. PMID: 29793344
-
How-to-guide for writing multiple choice questions for the pharmacy instructor.Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2017 Jan-Feb;9(1):137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.cptl.2016.08.036. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2017. PMID: 29180146 Review.
-
Twelve tips for introducing students to research and publishing: a medical student's perspective.Med Teach. 2012;34(9):705-9. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.684915. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22905656 Review.
Cited by
-
A scoping review of activities intended to reduce publication bias in randomised trials.Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 20;13(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02728-5. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39707441 Free PMC article.
-
Pedagogic Strategies and Contents in Medical Writing/Publishing Education: A Comprehensive Systematic Survey.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024 Sep 2;14(9):2491-2508. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14090165. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024. PMID: 39329833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peat J, Elliott E, Baur L, Keena V. BMJ Books. London: BMJ Books, London:Blackwell publishing; 2002. Scientific Writing: Easy When You Know How.
-
- Hekelman FP, Gilchrist V, Zyzanski SJ, Glover P, Olness K. An educational intervention to increase faculty publication productivity. Fam Med. 1995;27(4):255–9. - PubMed
-
- Yanoff KL, Burg FD. Types of medical writing and teaching of writing in U.S. medical schools. J Med Educ. 1988;63(1):30–7. - PubMed
-
- Nte AR, Awi DD. Writing a scientific paper: getting to the basics. Niger J Med. 2007;16(3):212–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

