Ex vivo infection of human embryonic spinal cord neurons prior to transplantation into adult mouse cord
- PMID: 20509957
- PMCID: PMC2890693
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-65
Ex vivo infection of human embryonic spinal cord neurons prior to transplantation into adult mouse cord
Abstract
Background: Genetically modified pseudorabies virus (Prv) proved suitable for the delivery of foreign genes to rodent embryonic neurons ex vivo and maintaining foreign gene expression after transplantation into spinal cord in our earlier study. The question arose of whether human embryonic neurons, which are known to be more resistant to Prv, could also be infected with a mutant Prv. Specifically, we investigated whether a mutant Prv with deleted ribonucleotide reductase and early protein 0 genes has the potential to deliver marker genes (gfp and beta-gal) into human embryonic spinal cord neurons and whether the infected neurons maintain expression after transplantation into adult mouse cord.
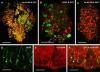
Results: The results revealed that the mutant Prv effectively infected human embryonic spinal cord neurons ex vivo and the grafted cells exhibited reporter gene expression for several weeks. Grafting of infected human embryonic cells into the spinal cord of immunodeficient (rnu-/rnu-) mice resulted in the infection of some of the host neurons.
Discussion: These results suggest that Prv is suitable for the delivery of foreign genes into transplantable human cells. This delivery method may offer a new approach to use genetically modified cells for grafting in animal models where spinal cord neuronal loss or axon degeneration occurs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pseudorabies virus-based gene delivery to rat embryonic spinal cord grafts.Hum Gene Ther. 2002 Apr 10;13(6):719-29. doi: 10.1089/104303402317322285. Hum Gene Ther. 2002. PMID: 11936971
-
Distribution of sympathetic preganglionic neurons innervating the kidney in the rat: PRV transneuronal tracing and serial reconstruction.Auton Neurosci. 2002 Jan 10;95(1-2):57-70. doi: 10.1016/s1566-0702(01)00356-3. Auton Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11871786
-
Characterization of a replication-incompetent pseudorabies virus mutant lacking the sole immediate early gene IE180.mBio. 2014 Nov 11;5(6):e01850. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01850-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25389174 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of human neurons (NT2N) grafted into mouse spinal cord: implications for improving therapy of spinal cord injury.Prog Brain Res. 2000;128:299-307. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)28027-8. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105689 Review.
-
[Studies on neuronal tracing with pseudorabies virus].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2014 May;30(3):333-7. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25118391 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Bartha A. Experimental reduction of virulence of Aujeszky's disease (in Hungarian) Magy Állatorv Lapja. 1961;16:42–45.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

