Early uptake and continuous accumulation of thallium-201 chloride in a benign mixed tumor of soft tissue: case report
- PMID: 20509963
- PMCID: PMC2887811
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-34
Early uptake and continuous accumulation of thallium-201 chloride in a benign mixed tumor of soft tissue: case report
Abstract
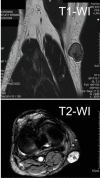
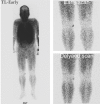
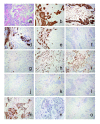
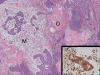
A case of benign mixed tumor of the soft tissue in a 64-year-old Japanese male is presented. He noticed a painless, elastic hard mass sized 3 cm in the right knee, which gradually grew larger and harder in the last 5 years. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a mass lesion embedded in the subcutaneous tissue with low and high signal intensity at T1- and T2-weighted images, respectively. Tl-201 scintigraphy showed an early uptake of Tl-201 within the lesion at 10 minutes after injection, which was slightly decreased but still continued at 2 hours later. The patient underwent a resection of tumor, and the pathological diagnosis was a benign mixed tumor of soft tissue without high vascularity, characterized by histological features similar to pleomorphic adenomas in the salivary glands. Immunohistochemical study proved expression of Na+/K+-ATPase of tumor cells. Overexpression of Na+/K+-ATPase of the tumor might be responsible for the early uptake of Tl-201, and poor vascular structure in this tumor might lead to continuous accumulation. The Tl-201 scintigraphic features of mixed tumor of soft tissue are assessed to resemble those of malignant soft tissue tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Delpire E, Gullans SR. Cell volume and K+ transport during differentiation of mouse erythroleukemia cells. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:C515–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

