A versatile approach to transform low-affinity peptides into protein probes with cotranslationally expressed chemical cross-linker
- PMID: 20510935
- PMCID: PMC2914685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.05.026
A versatile approach to transform low-affinity peptides into protein probes with cotranslationally expressed chemical cross-linker
Abstract
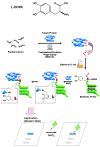
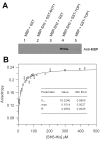
The potential usefulness of artificially selected peptides as probes to detect specific proteins has been proposed because of the ease and low cost of syntheses, manipulation, and genetic expression. However, the affinities of these peptides to their target proteins are generally too low to be practical as diagnostic or bioanalytical reagents. One approach to this problem is to incorporate a redox-active amino acid, 3,4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine (l-DOPA), that selectively forms a covalent linkage to the target protein. Such peptide-based probes can also be fused to tailored reporter proteins and easily expressed in bacterial cultures. As a demonstration, a candidate peptide, TOP1, that weakly binds to the target protein, the Src homology 3 (SH3) domain of human Abelson tyrosine kinase (Abl), was fused to green fluorescent protein (GFP) and l-DOPA was site-specifically incorporated into the peptide region (TOP1-DOPA-GFP). TOP1-DOPA-GFP produced from Escherichia coli was used in a Western blot-type experiment to show that the Abl SH3 domain can be detected in one step by observing the fluorescence. The molecular design presented in this work is significant in that the same approach could be used to transform many other protein-binding peptides with insufficient affinities into protein detection probes with a variety of fused reporter or therapeutic proteins.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


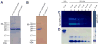
Similar articles
-
Examining the specificity of Src homology 3 domain--ligand interactions with alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins.Anal Biochem. 1997 Apr 5;247(1):143-51. doi: 10.1006/abio.1997.2040. Anal Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9126384
-
Distinct ligand preferences of Src homology 3 domains from Src, Yes, Abl, Cortactin, p53bp2, PLCgamma, Crk, and Grb2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1540-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1540. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8643668 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of the regulatory function of the c-Abl Src homology 3 domain.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 22;20(53):7744-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204978. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11753652
-
Engineered regulation of lysozyme by the SH3-CB1 binding interaction.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012 Jun;25(6):307-11. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzs020. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2012. PMID: 22532698
-
Crystal structure of the abl-SH3 domain complexed with a designed high-affinity peptide ligand: implications for SH3-ligand interactions.J Mol Biol. 1998 Aug 21;281(3):513-21. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1932. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9698566
Cited by
-
Structure-based non-canonical amino acid design to covalently crosslink an antibody-antigen complex.J Struct Biol. 2014 Feb;185(2):215-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 13. J Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 23680795 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and Genetic Incorporation of 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-Phenylalanine into Proteins in Escherichia coli.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 30;434(8):167412. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167412. Epub 2021 Dec 20. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34942167 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Incorporation of Biosynthesized L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and Its Application to Protein Conjugation.J Vis Exp. 2018 Aug 24;(138):58383. doi: 10.3791/58383. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30199031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Z, Zhu W, Kodadek T. Selection and application of peptide-binding peptides. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:71–4. - PubMed
-
- Kodadek T, Reddy MM, Olivos HJ, Bachhawat-Sikder K, Alluri PG. Synthetic molecules as antibody replacements. Acc Chem Res. 2004;37:711–8. - PubMed
-
- Smith GP, Petrenko VA. Phage Display. Chem Rev. 1997;97:391–410. - PubMed
-
- Lam KS, Lebl M, Krchnak V. The “One-Bead-One-Compound” Combinatorial Library Method. Chem Rev. 1997;97:411–448. - PubMed
-
- Franzosa E, Linghu B, Xia Y. Computational reconstruction of protein-protein interaction networks: algorithms and issues. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:89–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

