Evaluation of retinoic acid therapy for OTX2-positive medulloblastomas
- PMID: 20511190
- PMCID: PMC2940451
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nop062
Evaluation of retinoic acid therapy for OTX2-positive medulloblastomas
Abstract
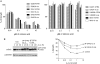
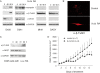
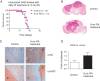
The homeobox transcription factor OTX2 plays an essential role during embryonic brain development. It is normally silenced in the adult brain, but is overexpressed by genomic amplification or other mechanisms in the majority of medulloblastomas (MBs). Retinoic acids (RAs) can suppress OTX2 expression and inhibit MB growth. In this study, 9-cis RA most potently inhibited MB cell growth. 9-cis RA functions through the downregulation of OTX2 expression, which subsequently induces neuronal differentiation of OTX2-expressing cells. Treatment with 9-cis RA reduced the growth of D425 flank xenograft tumors in mice. In an intracranial model, however, MB tumors showed resistance to 9-cis RA treatment, and we implicated fibroblast growth factor (FGF) as a potential mediator of resistance to RA therapy. These findings suggest a mechanism for RA-mediated anti-tumor effect on OTX2-positive MB cells and indicate that therapeutic targeting of OTX2 might be effective if FGF pathway-mediated resistance can be overcome.
Figures


References
-
- Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, et al. The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:215–225. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SL, Reddick WE, Gajjar A. Understanding the cognitive impact on children who are treated for medulloblastoma. J Pediatr Psychol. 2007;32:1040–1049. - PubMed
-
- Yokota N, Mainprize TG, Taylor MD, et al. Identification of differentially expressed and developmentally regulated genes in medulloblastoma using suppression subtraction hybridization. Oncogene. 2004;23:3444–3453. - PubMed
-
- Boon K, Eberhart CG, Riggins GJ. Genomic amplification of orthodenticle homologue 2 in medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:703–707. - PubMed
-
- Di C, Liao S, Adamson DC, et al. Identification of OTX2 as a medulloblastoma oncogene whose product can be targeted by all-trans-retinoic acid. Cancer Res. 2005;65:919–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

