Acute cobalt-induced lung injury and the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in modulating inflammation
- PMID: 20511350
- PMCID: PMC2905409
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq155
Acute cobalt-induced lung injury and the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in modulating inflammation
Abstract
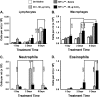
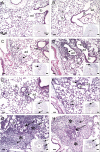
Air pollution is a critical factor in the development and exacerbation of pulmonary diseases. Ozone, automobile exhaust, cigarette smoke, and metallic dust are among the potentially harmful pollution components that are linked to disease progression. Transition metals, such as cobalt, have been identified at significant levels in air pollution. Cobalt exerts numerous biological effects, including mimicking hypoxia. Similar to hypoxia, cobalt exposure results in the stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), a family of proteins that regulate the cellular response to oxygen deficit. HIFs also play an important role in innate immunity and inflammatory processes. To characterize the role of HIF1alpha, the most ubiquitously expressed HIF, in the early events during cobalt-induced lung inflammation, an inducible lung-specific HIF1alpha deletion model was employed. Control mice showed classical signs of metal-induced injury following cobalt exposure, including neutrophilic infiltration and induction of Th1 cytokines. In contrast, HIF1alpha-deficient mice exhibited pronounced eosinophil counts in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and lung tissue complemented with Th2 cytokine induction. The timing of these results suggests that the loss of epithelial-derived HIF1alpha alters the lung's innate immune response and biases the tissue toward a Th2-mediated inflammation.
Figures
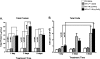


Comment in
-
Cobalt-Induced lung injury and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Nov;118(1):318; author reply 319. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq248. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20719750 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1{alpha} in modulating cobalt-induced lung inflammation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):L139-47. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00252.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19915160 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha in the lung alveolar epithelium of mice leads to enhanced eosinophilic inflammation in cobalt-induced lung injury.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Feb;137(2):447-57. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft253. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24218148 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α is a key mediator of the lung inflammatory potential of lithium-ion battery particles.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019 Sep 18;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12989-019-0319-z. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31533843 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen Sensing in Innate Immune Cells: How Inflammation Broadens Classical Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Regulation in Myeloid Cells.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Nov;37(13-15):956-971. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0004. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 35088604 Review.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and Its Role in Lung Injury: Adaptive or Maladaptive.Inflammation. 2023 Apr;46(2):491-508. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01769-z. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36596930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Up-regulation of Gadd45α after exposure to metal nanoparticles: the role of hypoxia inducible factor 1α.Environ Toxicol. 2015 Apr;30(4):490-9. doi: 10.1002/tox.21926. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Environ Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 24277352 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α-induced regulation of lung injury in pulmonary aspiration is mediated through NF-kB.FASEB Bioadv. 2022 Jan 12;4(5):309-328. doi: 10.1096/fba.2021-00132. eCollection 2022 May. FASEB Bioadv. 2022. PMID: 35520392 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 Mediates the Protective Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from iPSCs to Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Injury Under Hypoxia.Cell Transplant. 2018 Mar;27(3):571-583. doi: 10.1177/0963689718767159. Epub 2018 May 28. Cell Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29806480 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal epithelial hypoxia inducible factor-1α expression regulates the response of the lung to experimental asthma.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Mar 1;302(5):L455-62. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00193.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22180657 Free PMC article.
-
A novel multifunctional fluorescent probe with ESIPT and AIE effects for the detection of Co2+ and HClO.RSC Adv. 2025 Feb 6;15(6):4000-4013. doi: 10.1039/d4ra07451c. eCollection 2025 Feb 6. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 39926234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad-Nejad P, Mrabet-Dahbi S, Breuer K, Klotz M, Werfel T, Herz U, Heeg K, Neumaier M, Renz H. The toll-like receptor 2 R753Q polymorphism defines a subgroup of patients with atopic dermatitis having severe phenotype. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2004;113:565–567. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Bucher JR. NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of cobalt sulfate heptahydrate in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (Inhalation Studies) (CAS No. 10026-24-1) Toxic. Rep. Ser. 1991;5:1–38. - PubMed
-
- Bunn HF, Poyton RO. Oxygen sensing and molecular adaptation to hypoxia. Phys. Rev. 1996;76:839–885. - PubMed
-
- Elson DA, Ryan HE, Snow JW, Johnson R, Arbeit JM. Coordinate up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-1 target genes during multi-stage epidermal carcinogenesis and wound healing. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6189–6195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

