Disturbed expression of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex and associated signaling molecules in CD30+ T-cell lymphoproliferations
- PMID: 20511667
- PMCID: PMC2948095
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.021428
Disturbed expression of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex and associated signaling molecules in CD30+ T-cell lymphoproliferations
Abstract
Background: CD30(+) T-cell lymphoproliferations comprise a spectrum of clinically heterogeneous entities, including systemic anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALK(-) and ALK(+)) and primary cutaneous CD30(+) T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. While all these entities are characterized by proliferation of highly atypical, anaplastic CD30(+) T cells, the expression of T-cell specific antigens in the tumor cells is not consistently detectable.
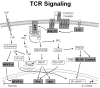
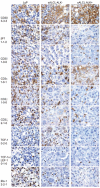
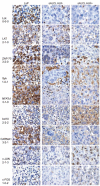
Design and methods: We evaluated biopsies from 19 patients with primary cutaneous CD30(+) lymphoproliferative disorders, 38 with ALK(-) and 33 with ALK(+) systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. The biopsies were examined for the expression of T-cell receptorαβ/CD3 complex (CD3γ, δ, ε, ζ), transcription factors regulating T-cell receptor expression (ATF1, ATF2, TCF-1, TCF-1α/LEF-1, Ets1), and molecules of T-cell receptor-associated signaling cascades (Lck, ZAP-70, LAT, bcl-10, Carma1, NFATc1, c-Jun, c-Fos, Syk) using immunohistochemistry.
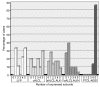
Results: In comparison to the pattern in 20 peripheral T-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified, we detected a highly disturbed expression of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex, TCF-1, TCF-1α/LEF-1, Lck, ZAP-70, LAT, NFATc1, c-Jun, c-Fos and Syk in most of the systemic anaplastic large cell lymphomas. In addition, primary cutaneous CD30(+) lymphoproliferative disorders showed such a similar expression pattern to that of systemic anaplastic large cell lymphomas, that none of the markers we investigated can reliably distinguish between these CD30(+) T-cell lymphoproliferations.
Conclusions: Severely altered expression of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex, T-cell receptor-associated transcription factors and signal transduction molecules is a common characteristic of systemic and cutaneous CD30(+) lymphoproliferations, although the clinical behavior of these entities is very different. Since peripheral T-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified retain the full expression program required for functioning T-cell receptor signaling, the differential expression of a subset of these markers might be of diagnostic utility in distinguishing peripheral T-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified from the entire group of CD30(+) lymphoproliferations.
Figures
Comment in
-
CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders.Haematologica. 2010 Oct;95(10):1627-30. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.029256. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20884717 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bonzheim I, Geissinger E, Roth S, Zettl A, Marx A, Rosenwald A, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphomas lack the expression of T-cell receptor molecules or molecules of proximal T-cell receptor signaling. Blood. 2004;104(10):3358–60. - PubMed
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124–30. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SHCE, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008.
-
- Yu JB, Blitzblau RC, Decker RH, Housman DM, Wilson LD. Analysis of primary CD30+ cutaneous lymphoproliferative disease and survival from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(9):1483–8. - PubMed
-
- Kempf W. CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders: histopathology, differential diagnosis, new variants, and simulators. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33 (Suppl 1):58–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

