Importance of polyadenylation in the selective elimination of meiotic mRNAs in growing S. pombe cells
- PMID: 20512112
- PMCID: PMC2905246
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.108
Importance of polyadenylation in the selective elimination of meiotic mRNAs in growing S. pombe cells
Abstract
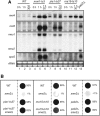
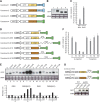
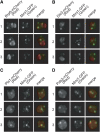
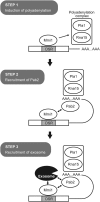
A number of meiosis-specific mRNAs are initially weakly transcribed, but then selectively removed during fission yeast mitotic growth. These mRNAs harbour a region termed DSR (determinant of selective removal), which is recognized by the YTH family RNA-binding protein Mmi1p. Mmi1p directs the destruction of these mRNAs in collaboration with nuclear exosomes. However, detailed molecular mechanisms underlying this process of selective mRNA elimination have remained elusive. In this study, we demonstrate the critical role of polyadenylation in this process. Two-hybrid and genetic screens revealed potential interactions between Mmi1p and proteins involved in polyadenylation. Additional investigations showed that destruction of DSR-containing mRNAs by exosomes required polyadenylation by a canonical poly(A) polymerase. The recruitment of Pab2p, a poly(A)-binding protein, to the poly(A) tail was also necessary for mRNA destruction. In cells undergoing vegetative growth, Mmi1p localized with exosomes, Pab2p, and components of the polyadenylation complex in several patchy structures in the nucleoplasm. These patches may represent the sites for degradation of meiosis-specific mRNAs with untimely expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hexanucleotide motifs mediate recruitment of the RNA elimination machinery to silent meiotic genes.Open Biol. 2012 Mar;2(3):120014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120014. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22645662 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the specific recognition of DSR by the YTH domain containing protein Mmi1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):310-316. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.104. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28735863
-
Selective elimination of messenger RNA prevents an incidence of untimely meiosis.Nature. 2006 Jul 6;442(7098):45-50. doi: 10.1038/nature04881. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16823445
-
The selective elimination of messenger RNA underlies the mitosis-meiosis switch in fission yeast.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(8):788-97. doi: 10.2183/pjab.86.788. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20948174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cid1 family of non-canonical poly(A) polymerases.Yeast. 2006 Oct 15;23(13):991-1000. doi: 10.1002/yea.1408. Yeast. 2006. PMID: 17072891 Review.
Cited by
-
DEAD-box ATPase Dbp2 is the key enzyme in an mRNP assembly checkpoint at the 3'-end of genes and involved in the recycling of cleavage factors.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 9;15(1):6829. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51035-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39122693 Free PMC article.
-
The human nuclear poly(a)-binding protein promotes RNA hyperadenylation and decay.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(10):e1003893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003893. Epub 2013 Oct 17. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24146636 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation and functions of the nuclear RNA exosome complex.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;17(4):227-39. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.15. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26726035 Review.
-
Hexanucleotide motifs mediate recruitment of the RNA elimination machinery to silent meiotic genes.Open Biol. 2012 Mar;2(3):120014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120014. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22645662 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA exosome contributes to gene expression regulation during stem cell differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 30;46(21):11502-11513. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky817. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30212902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bähler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A III, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14: 943–951 - PubMed
-
- Briggs MW, Burkard KT, Butler JS (1998) Rrp6p, the yeast homologue of the human PM-Scl 100-kDa autoantigen, is essential for efficient 5.8 S rRNA 3′ end formation. J Biol Chem 273: 13255–13263 - PubMed
-
- Bühler M, Haas W, Gygi SP, Moazed D (2007) RNAi-dependent and -independent RNA turnover mechanisms contribute to heterochromatic gene silencing. Cell 129: 707–721 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

