A novel ATP-dependent conformation in p97 N-D1 fragment revealed by crystal structures of disease-related mutants
- PMID: 20512113
- PMCID: PMC2905243
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.104
A novel ATP-dependent conformation in p97 N-D1 fragment revealed by crystal structures of disease-related mutants
Abstract
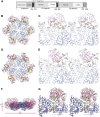
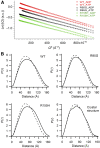
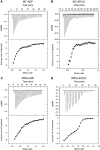
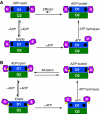
Mutations in p97, a major cytosolic AAA (ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities) chaperone, cause inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget's disease of the bone and frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD). IBMPFD mutants have single amino-acid substitutions at the interface between the N-terminal domain (N-domain) and the adjacent AAA domain (D1), resulting in a reduced affinity for ADP. The structures of p97 N-D1 fragments bearing IBMPFD mutations adopt an atypical N-domain conformation in the presence of Mg(2+).ATPgammaS, which is reversible by ADP, showing for the first time the nucleotide-dependent conformational change of the N-domain. The transition from the ADP- to the ATPgammaS-bound state is accompanied by a loop-to-helix conversion in the N-D1 linker and by an apparent re-ordering in the N-terminal region of p97. X-ray scattering experiments suggest that wild-type p97 subunits undergo a similar nucleotide-dependent N-domain conformational change. We propose that IBMPFD mutations alter the timing of the transition between nucleotide states by destabilizing the ADP-bound form and consequently interfere with the interactions between the N-domains and their substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered intersubunit communication is the molecular basis for functional defects of pathogenic p97 mutants.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36624-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.488924. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24196964 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the N-domain in the ATPase activity of the mammalian AAA ATPase p97/VCP.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):8561-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.302778. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22270372 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional deviations in disease-associated p97 mutants.J Struct Biol. 2012 Aug;179(2):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.04.024. Epub 2012 May 8. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22579784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D1 ring is stable and nucleotide-independent, whereas D2 ring undergoes major conformational changes during the ATPase cycle of p97-VCP.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 29;278(35):32784-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303869200. Epub 2003 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12807884
-
ATP-bound form of the D1 AAA domain inhibits an essential function of Cdc48p/p97.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;88(1):109-17. doi: 10.1139/o09-116. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20130684 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural characterization of full-length NSF and 20S particles.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Feb 5;19(3):268-75. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2237. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22307055
-
The structural and functional basis of the p97/valosin-containing protein (VCP)-interacting motif (VIM): mutually exclusive binding of cofactors to the N-terminal domain of p97.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38679-38690. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274506. Epub 2011 Sep 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21914798 Free PMC article.
-
The UBX domain in UBXD1 organizes ubiquitin binding at the C-terminus of the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 5;14(1):3258. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38604-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37277335 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic Compromises Both p97 and Proteasome Functions.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Jul 17;30(7):1508-1514. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00158. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28636814 Free PMC article.
-
The Cryo-EM Effect: Structural Biology of Neurodegenerative Disease Proteostasis Factors.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2021 Jun 4;80(6):494-513. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlab029. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33860329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beuron F, Flynn TC, Ma J, Kondo H, Zhang X, Freemont PS (2003) Motions and negative cooperativity between p97 domains revealed by cryo-electron microscopy and quantised elastic deformational model. J Mol Biol 327: 619–629 - PubMed
-
- Dai RM, Li CC (2001) Valosin-containg protein is a multi-ubiquitin chain-targeting factor required in ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Nat Cell Biol 3: 740–744 - PubMed
-
- Davies JM, Tsuruta H, May AP, Weis WI (2005) Conformational changes of p97 during nucleotide hydrolysis determined by small-angle X-ray scattering. Structure 13: 183–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

