Prp43p contains a processive helicase structural architecture with a specific regulatory domain
- PMID: 20512115
- PMCID: PMC2905241
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.102
Prp43p contains a processive helicase structural architecture with a specific regulatory domain
Abstract
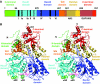
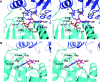
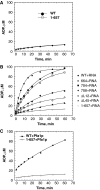
The DEAH/RNA helicase A (RHA) helicase family comprises proteins involved in splicing, ribosome biogenesis and transcription regulation. We report the structure of yeast Prp43p, a DEAH/RHA helicase remarkable in that it functions in both splicing and ribosome biogenesis. Prp43p displays a novel structural architecture with an unforeseen homology with the Ski2-like Hel308 DNA helicase. Together with the presence of a beta-hairpin in the second RecA-like domain, Prp43p contains all the structural elements of a processive helicase. Moreover, our structure reveals that the C-terminal domain contains an oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding (OB)-fold placed at the entrance of the putative nucleic acid cavity. Deletion or mutations of this domain decrease the affinity of Prp43p for RNA and severely reduce Prp43p ATPase activity in the presence of RNA. We also show that this domain constitutes the binding site for the G-patch-containing domain of Pfa1p. We propose that the C-terminal domain, specific to DEAH/RHA helicases, is a central player in the regulation of helicase activity by binding both RNA and G-patch domain proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structure of the DEAH/RHA ATPase Prp43p bound to RNA implicates a pair of hairpins and motif Va in translocation along RNA.RNA. 2017 Jul;23(7):1110-1124. doi: 10.1261/rna.060954.117. Epub 2017 Apr 17. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28416566 Free PMC article.
-
The ATPase and helicase activities of Prp43p are stimulated by the G-patch protein Pfa1p during yeast ribosome biogenesis.EMBO J. 2009 Dec 16;28(24):3808-19. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.335. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19927118 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the function of DEAH helicases.EMBO Rep. 2010 Mar;11(3):180-6. doi: 10.1038/embor.2010.11. Epub 2010 Feb 19. EMBO Rep. 2010. PMID: 20168331 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DEAH/RHA helicases by G-patch proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:931857. doi: 10.1155/2015/931857. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25692149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of DEAH-box RNA helicases by G-patch proteins.Biol Chem. 2021 Jan 6;402(5):561-579. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2020-0338. Print 2021 Apr 27. Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33857358 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo analysis of the interaction between RNA helicase A and HIV-1 RNA.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(24):13272-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01993-12. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23015696 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between RNA helicase ROOT INITIATION DEFECTIVE 1 and GAMETOPHYTIC FACTOR 1 is involved in female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Oct;67(19):5757-5768. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw341. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27683728 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of individual domains in the function of DHX29, an essential factor required for translation of structured mammalian mRNAs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 13;109(46):E3150-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208014109. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23047696 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for RNA translocation by DEAH-box ATPases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 7;47(8):4349-4362. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz150. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30828714 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of cis- and trans-regulatory mechanisms in the spliceosomal RNA helicase Brr2.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jan 2;16(1):100-112. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1255384. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 27880071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams JP, Leslie AG (1996) Methods used in the structure determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 52: 30–42 - PubMed
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV (1999) G-patch: a new conserved domain in eukaryotic RNA-processing proteins and type D retroviral polyproteins. Trends Biochem Sci 24: 342–344 - PubMed
-
- Arcus V (2002) OB-fold domains: a snapshot of the evolution of sequence, structure and function. Curr Opin Struct Biol 12: 794–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

