Enhanced neuronal RNAi in C. elegans using SID-1
- PMID: 20512143
- PMCID: PMC2894993
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1463
Enhanced neuronal RNAi in C. elegans using SID-1
Abstract
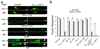
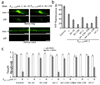
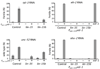
We expressed SID-1, a transmembrane protein from Caenorhabditis elegans that is required for systemic RNA interference (RNAi), in C. elegans neurons. This expression increased the response of neurons to double-stranded (ds)RNA delivered by feeding. Mutations in the lin-15b and lin-35 genes enhanced this effect. Worms expressing neuronal SID-1 showed RNAi phenotypes when fed with bacteria expressing dsRNA for known neuronal genes and for uncharacterized genes with no previously known neuronal phenotypes. Neuronal expression of sid-1 decreased nonneuronal RNAi, suggesting that neurons expressing transgenic sid-1(+) served as a sink for dsRNA. This effect, or a sid-1(-) background, can be used to uncover neuronal defects for lethal genes. Expression of sid-1(+) from cell-specific promoters in sid-1 mutants results in cell-specific feeding RNAi. We used these strains to identify a role for integrin signaling genes in mechanosensation.
Figures
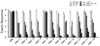
Similar articles
-
Optimization of RNAi efficiency in PVD neuron of C. elegans.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 18;19(3):e0298766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298766. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38498505 Free PMC article.
-
SID-1 Functions in Multiple Roles To Support Parental RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 Oct;207(2):547-557. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300067. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28751423 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:95-100. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.060. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381285 Review.
-
SID-4/NCK-1 is important for dsRNA import in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Nov 4;12(11):jkac252. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac252. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 36165710 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Perspective of the Double-Stranded RNA Transport Mechanism by SID-1 Family Proteins.Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(10):1610-1615. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b24-00419. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39358240 Review.
Cited by
-
Double-stranded RNA made in C. elegans neurons can enter the germline and cause transgenerational gene silencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 17;112(7):2133-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423333112. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25646479 Free PMC article.
-
A novel de novo FEM1C variant is linked to neurodevelopmental disorder with absent speech, pyramidal signs and limb ataxia.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Mar 20;32(7):1152-1161. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac276. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36336956 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in nervous system function and disease: using C. elegans as a dissecting tool.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(16):2691-715. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0946-0. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22382927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-GlcNAc signaling increases neuron regeneration through one-carbon metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans.Elife. 2024 Feb 9;13:e86478. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86478. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38334260 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans Models to Study the Propagation of Prions and Prion-Like Proteins.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 15;10(8):1188. doi: 10.3390/biom10081188. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32824215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Tabara H, Grishok A, Mello CC. RNAi in C. elegans: soaking in the genome sequence. Science. 1998;282:430–431. - PubMed
-
- Timmons L, Fire A. Specific interference by ingested dsRNA. Nature. 1998;395:854. - PubMed
-
- Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Zipperlen P, Martinez-Campos M, Sohrmann M, Ahringer J. Functional genomic analysis of C. elegans chromosome I by systematic RNA interference. Nature. 2000;408:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Kamath RS, Fraser AG, Dong Y, Poulin G, Durbin R, Gotta M, Kanapin A, Le Bot N, Moreno S, Sohrmann M, et al. Systematic functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature. 2003;421:231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

