Mutations in TMEM216 perturb ciliogenesis and cause Joubert, Meckel and related syndromes
- PMID: 20512146
- PMCID: PMC2894012
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.594
Mutations in TMEM216 perturb ciliogenesis and cause Joubert, Meckel and related syndromes
Abstract
Joubert syndrome (JBTS), related disorders (JSRDs) and Meckel syndrome (MKS) are ciliopathies. We now report that MKS2 and CORS2 (JBTS2) loci are allelic and caused by mutations in TMEM216, which encodes an uncharacterized tetraspan transmembrane protein. Individuals with CORS2 frequently had nephronophthisis and polydactyly, and two affected individuals conformed to the oro-facio-digital type VI phenotype, whereas skeletal dysplasia was common in fetuses affected by MKS. A single G218T mutation (R73L in the protein) was identified in all cases of Ashkenazi Jewish descent (n=10). TMEM216 localized to the base of primary cilia, and loss of TMEM216 in mutant fibroblasts or after knockdown caused defective ciliogenesis and centrosomal docking, with concomitant hyperactivation of RhoA and Dishevelled. TMEM216 formed a complex with Meckelin, which is encoded by a gene also mutated in JSRDs and MKS. Disruption of tmem216 expression in zebrafish caused gastrulation defects similar to those in other ciliary morphants. These data implicate a new family of proteins in the ciliopathies and further support allelism between ciliopathy disorders.
Figures
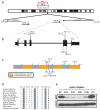
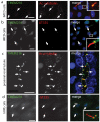

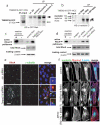

Comment in
-
TMEM216 joins its ciliary cousins in ciliopathies.Clin Genet. 2011 Jan;79(1):45-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2010.01556_2.x. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Clin Genet. 2011. PMID: 21029074 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
TMEM237 is mutated in individuals with a Joubert syndrome related disorder and expands the role of the TMEM family at the ciliary transition zone.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Dec 9;89(6):713-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.005. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 22152675 Free PMC article.
-
Defects in diffusion barrier function of ciliary transition zone caused by ciliopathy variations of TMEM218.Hum Mol Genet. 2024 Aug 6;33(16):1442-1453. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddae083. Hum Mol Genet. 2024. PMID: 38751342
-
Variable expressivity of ciliopathy neurological phenotypes that encompass Meckel-Gruber syndrome and Joubert syndrome is caused by complex de-regulated ciliogenesis, Shh and Wnt signalling defects.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Apr 1;22(7):1358-72. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds546. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23283079 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics and pathogenic mechanisms for the severe ciliopathies: insights into neurodevelopment and pathogenesis of neural tube defects.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Feb;43(1):12-26. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8154-0. Epub 2010 Nov 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21110233 Review.
-
The Joubert-Meckel-Nephronophthisis Spectrum of Ciliopathies.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2022 Aug 31;23:301-329. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-121321-093528. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35655331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental disruptions underlying brain abnormalities in ciliopathies.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 24;6:7857. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8857. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26206566 Free PMC article.
-
Classification, clinical features, and genetics of neural tube defects.Saudi Med J. 2014 Dec;35 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S5-S14. Saudi Med J. 2014. PMID: 25551113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meckelin is necessary for photoreceptor intraciliary transport and outer segment morphogenesis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Feb 23;53(2):967-74. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8766. Print 2012 Feb. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22247471 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer systems biology of TCGA SKCM: efficient detection of genomic drivers in melanoma.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 20;5:7857. doi: 10.1038/srep07857. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25600636 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in human C2CD3 cause skeletal dysplasia and provide new insights into phenotypic and cellular consequences of altered C2CD3 function.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 20;6:24083. doi: 10.1038/srep24083. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27094867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valente EM, et al. Distinguishing the four genetic causes of Joubert syndrome-related disorders. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:513–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0700073/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GGP08145/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- R01 NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075972/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK079541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042601/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0700073(81627)/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD04260/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS04843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

