Visualizing vascular permeability and lymphatic drainage using labeled serum albumin
- PMID: 20512410
- PMCID: PMC2921845
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-010-9170-4
Visualizing vascular permeability and lymphatic drainage using labeled serum albumin
Abstract
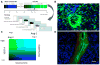
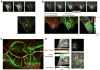
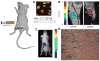
During the early stages of angiogenesis, following stimulation of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), the vascular wall is breached, allowing high molecular weight proteins to leak from the vessels to the interstitial space. This hallmark of angiogenesis results in deposition of a provisional matrix, elevation of the interstitial pressure and induction of interstitial convection. Albumin, the major plasma protein appears to be an innocent bystander that is significantly affected by these changes, and thus can be used as a biomarker for vascular permeability associated with angiogenesis. Traditionally, albumin leak in superficial organs was followed by colorimetry or morphometry with the use of albumin binding vital dyes. Over the last years, the introduction of tagged-albumin that can be detected by various imaging methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography, opened new possibilities for quantitative three dimension dynamic analysis of permeability in any organ. Using these tools it is now possible to follow not only vascular permeability, but also interstitial convection and lymphatic drain. Active uptake of tagged albumin by caveolae-mediated endocytosis opens the possibility for using labeled albumin for vital staining of cells and cell tracking. This approach was used for monitoring recruitment of perivascular stroma fibroblasts associated with tumor angiogenesis.
Figures
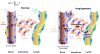

References
-
- Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989;246:1306–1309. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF. Discovery of vascular permeability factor (VPF) Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:522–526. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak HF, Nagy JA, Feng D, et al. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and the significance of microvascular hyperpermeability in angiogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;237:97–132. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak AM, Feng D. The vesiculo-vacuolar organelle (VVO). A new endothelial cell permeability organelle. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49:419–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

