Quantitative sodium imaging with a flexible twisted projection pulse sequence
- PMID: 20512862
- PMCID: PMC2879672
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22381
Quantitative sodium imaging with a flexible twisted projection pulse sequence
Abstract
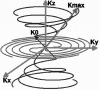
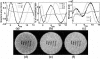
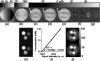
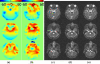
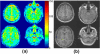
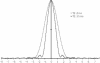
The quantification of sodium MR images from an arbitrary intensity scale into a bioscale fosters image interpretation in terms of the spatially resolved biochemical process of sodium ion homeostasis. A methodology for quantifying tissue sodium concentration using a flexible twisted projection imaging sequence is proposed that allows for optimization of tradeoffs between readout time, signal-to-noise ratio efficiency, and sensitivity to static field susceptibility artifacts. The gradient amplitude supported by the slew rate at each k-space radius regularizes the readout gradient waveform design to avoid slew rate violation. Static field inhomogeneity artifacts are corrected using a frequency-segmented conjugate phase reconstruction approach, with field maps obtained quickly from coregistered proton imaging. High-quality quantitative sodium images have been achieved in phantom and volunteer studies with real isotropic spatial resolution of 7.5 x 7.5 x 7.5 mm(3) for the slow T(2) component in approximately 8 min on a clinical 3-T scanner. After correcting for coil sensitivity inhomogeneity and water fraction, the tissue sodium concentration in gray matter and white matter was measured to be 36.6 +/- 0.6 micromol/g wet weight and 27.6 +/- 1.2 micromol/g wet weight, respectively.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

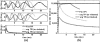
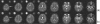

References
-
- Skou J. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957;23:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Lodish HF. Molecular cell biology. Scientific American Books; New York: 1999. p. 973.
-
- Thulborn KR, Davis D, Snyder J, Yonas H, Kassam A, Sodium MR. Imaging of Acute and Subacute Stroke for Assessment of Tissue Viability. Neuroimag Clin N Am. 2005;15:639–653. - PubMed
-
- Thulborn KR, Gindin TS, Davis D, Erb P. Comprehensive MRI Protocol for Stroke Management: Tissue Sodium Concentration as a Measure of Tissue Viability in a Non-Human Primate Model and Clinical Studies. Radiology. 1999;139:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith M, Damadian R. NMR in cancer. Physiol Chem Phys. 1975;7:263–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

