Smurf control in bone cells
- PMID: 20512916
- PMCID: PMC2886145
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22586
Smurf control in bone cells
Abstract
The homologous to the E6-associated protein carboxyl terminus (HECT) domain E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 is the first E3 ligase to be implicated in regulating bone cell function. The involvement of Smurf1 in multiple signaling pathways and pathological conditions is presently an area of extensive scientific interest. This review highlights recent works exploring Smurf-regulated biological processes in bone cells and highlights recent discoveries surrounding the regulatory mechanisms modulating its catalytic activity and substrate recognition capability. Moreover, we discuss the relevance of targeting the HECT E3s through the development of small-molecule inhibitors as an anticancer therapeutic strategy.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
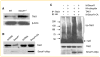
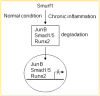
References
-
- Ballock RT, Heydemann A, Wakefield LM, Flanders KC, Roberts AB, Sporn MB. TGF-beta 1 prevents hypertrophy of epiphyseal chondrocytes: regulation of gene expression for cartilage matrix proteins and metalloproteases. Dev Biol. 1993;158(2):414–429. - PubMed
-
- Bassuk AG, Wallace RH, Buhr A, Buller AR, Afawi Z, Shimojo M, Miyata S, Chen S, Gonzalez-Alegre P, Griesbach HL, Wu S, Nashelsky M, Vladar EK, Antic D, Ferguson PJ, Cirak S, Voit T, Scott MP, Axelrod JD, Gurnett C, Daoud AS, Kivity S, Neufeld MY, Mazarib A, Straussberg R, Walid S, Korczyn AD, Slusarski DC, Berkovic SF, El-Shanti HI. A homozygous mutation in human PRICKLE1 causes an autosomal-recessive progressive myoclonus epilepsy-ataxia syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83(5):572–581. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernassola F, Karin M, Ciechanover A, Melino G. The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: multiple players in cancer development. Cancer Cell. 2008;14(1):10–21. - PubMed
-
- Bonni S, Wang HR, Causing CG, Kavsak P, Stroschein SL, Luo K, Wrana JL. TGF-beta induces assembly of a Smad2-Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets SnoN for degradation. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(6):587–595. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Dong XY, Sethi P, Cheng X, Zhou J, Ling J, Simons JW, Lingrel JB, Dong JT. Human Kruppel-like factor 5 is a target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 for proteolysis in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(50):41553–41561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

