Biology and pathology of Rho GTPase, PI-3 kinase-Akt, and MAP kinase signaling pathways in chondrocytes
- PMID: 20512918
- PMCID: PMC2883292
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22604
Biology and pathology of Rho GTPase, PI-3 kinase-Akt, and MAP kinase signaling pathways in chondrocytes
Abstract
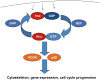
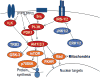
Chondrocytes provide the framework for the developing skeleton and regulate long-bone growth through the activity of the growth plate. Chondrocytes in the articular cartilage, found at the ends of bones in diarthroidial joints, are responsible for maintenance of the tissue through synthesis and degradation of the extracellular matrix. The processes of growth, differentiation, cell death and matrix remodeling are regulated by a network of cell signaling pathways in response to a variety of extracellular stimuli. These stimuli consist of soluble ligands, including growth factors and cytokines, extracellular matrix proteins, and mechanical factors that act in concert to regulate chondrocyte function through a variety of canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Key chondrocyte signaling pathways include, but are not limited to, the p38, JNK and ERK MAP kinases, the PI-3 kinase-Akt pathway, the Jak-STAT pathway, Rho GTPases and Wnt-beta-catenin and Smad pathways. Modulation of the activity of any of these pathways has been associated with various pathological states in cartilage. This review focuses on the Rho GTPases, the PI-3 kinase-Akt pathway, and some selected aspects of MAP kinase signaling. Most studies to date have examined these pathways in isolation but it is becoming clear that there is significant cross-talk among the pathways and that the overall effects on chondrocyte function depend on the balance in activity of multiple signaling proteins.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Appleton CT, Usmani SE, Mort JS, Beier F. Rho/ROCK and MEK/ERK activation by transforming growth factor-alpha induces articular cartilage degradation. Lab Invest. 2010;90:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Bobacz K, Sunk IG, Hofstaetter JG, Amoyo L, Toma CD, Akira S, Weichhart T, Saemann M, Smolen JS. Toll-like receptors and chondrocytes: the lipopolysaccharide-induced decrease in cartilage matrix synthesis is dependent on the presence of toll-like receptor 4 and antagonized by bone morphogenetic protein 7. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1880–93. - PubMed
-
- Bobick BE, Kulyk WM. Regulation of cartilage formation and maturation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Birth Defects Research Part C: Embryo Today: Reviews. 2008;84:131–154. - PubMed
-
- Boehm AK, Seth M, Mayr KG, Fortier LA. Hsp90 mediates insulin-like growth factor 1 and interleukin-1beta signaling in an age-dependent manner in equine articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2335–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

