Dissecting the cAMP-inducible allosteric switch in protein kinase A RIalpha
- PMID: 20512974
- PMCID: PMC2895245
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.400
Dissecting the cAMP-inducible allosteric switch in protein kinase A RIalpha
Abstract
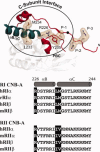
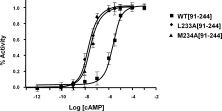
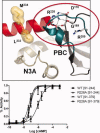
The regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) are the major receptors of cAMP in most eukaryotic cells. As the cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB) domains release cAMP and bind to the catalytic subunit of PKA, they undergo a major conformational change. The change is mediated by the B/C helix in CNB-A, which extends into one long helix that now separates the two CNB domains and docks onto the surface of the catalytic subunit. We explore here the role of three key residues on the B/C helix that dock onto the catalytic subunit, Arg226, Leu233, and Met 234. By replacing each residue with Ala, we show that each contributes significantly to creating the R:C interface. By also deleting the second CNB domain (CNB-B), we show furthermore that CNB-B is a critical part of the cAMP-induced conformational switch that dislodges the B/C helix from the surface of the catalytic subunit. Without CNB-B the K(a) for activation by cAMP increases from 80 to 1000 nM. Replacing any of the key interface residues with Ala reduces the K(a) to 25-40 nM. Leu233 and M234 contribute to a hydrophobic latch that binds the B/C helix onto the large lobe of the C-subunit, while Arg226 is part of an electrostatic switch that couples the B/C helix to the phosphate binding cassette where the cAMP docks.
Figures
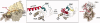

References
-
- Canaves JM, Taylor SS. Classification and phylogenetic analysis of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit family. J Mol Evol. 2002;54:17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

