Similarities between Argonautes and the alpha-sarcin-like ribotoxins: Implications for microRNA action
- PMID: 20512980
- PMCID: PMC2895252
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.391
Similarities between Argonautes and the alpha-sarcin-like ribotoxins: Implications for microRNA action
Abstract
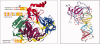
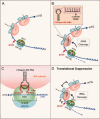
We report structural, functional, and biochemical similarities between Argonautes, the effector proteins of RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs), and alpha-sarcin-like ribotoxins. At the structural level, regions of similarity in the amino acid sequence are located in protein loops both in the ribotoxins and in the Argonautes. In ribotoxins, these protein loops confer specificity for a highly conserved segment of ribosomal RNA, the Sarcin-Ricin-Loop (SRL) that undergoes cleavage by the ribotoxin ribonuclease. This leads to suppression of translation. In addition to the structural similarity with ribotoxins, the Argonaute proteins (Ago) show both functional and biochemical parallels. Like the ribotoxins, the Agos exhibit ribonuclease activity and like the ribotoxins, translational suppression mediated by miRISC-resident Ago is accompanied by intact polysomes. Furthermore, in both translationally suppressed systems, the puromycin reaction, reflecting correct translocation and peptidyl-transferase activities, is unharmed. These findings support a mechanism for Ago-miRISCs whereby regulated cleavage of ribosomal RNA leads to translational suppression.
Figures

References
-
- Lamy B, Davies J, Schindler D. The Aspergillus ribonucleolytic toxins (ribotoxins) Targeted Diagn Ther. 1992;7:237–258. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Wool IG. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:9054–9060. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Mitsui K, Motizuki M, Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:5908–5912. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:8128–8130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

