Causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury using a structured expert opinion process: comparison to the Roussel-Uclaf causality assessment method
- PMID: 20512999
- PMCID: PMC3249230
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23577
Causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury using a structured expert opinion process: comparison to the Roussel-Uclaf causality assessment method
Abstract
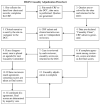
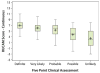
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is largely a diagnosis of exclusion and is therefore challenging. The US Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN) prospective study used two methods to assess DILI causality: a structured expert opinion process and the Roussel-Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM). Causality assessment focused on detailed clinical and laboratory data from patients with suspected DILI. The adjudication process used standardized numerical and descriptive definitions and scored cases as definite, highly likely, probable, possible, or unlikely. Results of the structured expert opinion procedure were compared with those derived by the RUCAM approach. Among 250 patients with suspected DILI, the expert opinion adjudication process scored 78 patients (31%) as definite, 102 (41%) as highly likely, 37 (15%) as probable, 25 (10%) as possible, and 8 (3%) as unlikely. Among 187 enrollees who had received a single implicated drug, initial complete agreement was reached for 50 (27%) with the expert opinion process and for 34 (19%) with a five-category RUCAM scale (P = 0.08), and the two methods demonstrated a modest correlation with each other (Spearman's r = 0.42, P = 0.0001). Importantly, the RUCAM approach substantially shifted the causality likelihood toward lower probabilities in comparison with the DILIN expert opinion process.
Conclusion: The structured DILIN expert opinion process produced higher agreement rates and likelihood scores than RUCAM in assessing causality, but there was still considerable interobserver variability in both. Accordingly, a more objective, reliable, and reproducible means of assessing DILI causality is still needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
Figures
References
-
- Zimmerman HJ. Drug-induced liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:73–96. - PubMed
-
- Sgro C, Clinard F, Ouazir K, Chanay H, Allard C, Guilleminet C, et al. Incidence of drug-induced hepatic injuries: a French population-based study. Hepatology. 2002;36:451–455. - PubMed
-
- Galan MV, Potts JA, Silverman AL, Gordon SC. The burden of acute nonfulminant drug-induced hepatitis in a United States tertiary referral center [corrected] J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:64–67. - PubMed
-
- Vuppalanchi R, Liangpunsakul S, Chalasani N. Etiology of new-onset jaundice: how often is it caused by idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury in the United States? Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:558–562. - PubMed
-
- Carey EJ, Vargas HE, Douglas DD, Balan V, Byrne TJ, Harrison ME, et al. Inpatient admissions for drug-induced liver injury: results from a single center. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:1977–1982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK065211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK065201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DK065184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
