Clinic-based treatment of opioid-dependent HIV-infected patients versus referral to an opioid treatment program: A randomized trial
- PMID: 20513828
- PMCID: PMC2886293
- DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-11-201006010-00003
Clinic-based treatment of opioid-dependent HIV-infected patients versus referral to an opioid treatment program: A randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Opioid dependence is common in HIV clinics. Buprenorphine-naloxone (BUP) is an effective treatment of opioid dependence that may be used in routine medical settings.
Objective: To compare clinic-based treatment with BUP (clinic-based BUP) with case management and referral to an opioid treatment program (referred treatment).
Design: Single-center, 12-month randomized trial. Participants and investigators were aware of treatment assignments. (ClinicalTrials.gov registration number: NCT00130819)
Setting: HIV clinic in Baltimore, Maryland.
Patients: 93 HIV-infected, opioid-dependent participants who were not receiving opioid agonist therapy and were not dependent on alcohol or benzodiazepines.
Intervention: Clinic-based BUP included BUP induction and dose titration, urine drug testing, and individual counseling. Referred treatment included case management and referral to an opioid-treatment program.
Measurements: Initiation and long-term receipt of opioid agonist therapy, urine drug test results, visit attendance with primary HIV care providers, use of antiretroviral therapy, and changes in HIV RNA levels and CD4 cell counts.
Results: The average estimated participation in opioid agonist therapy was 74% (95% CI, 61% to 84%) for clinic-based BUP and 41% (CI, 29% to 53%) for referred treatment (P < 0.001). Positive test results for opioids and cocaine were significantly less frequent in clinic-based BUP than in referred treatment, and study participants receiving clinic-based BUP attended significantly more HIV primary care visits than those receiving referred treatment. Use of antiretroviral therapy and changes in HIV RNA levels and CD4 cell counts did not differ between the 2 groups.
Limitation: This was a small single-center study, follow-up was only moderate, and the study groups were unbalanced in terms of recent drug injections at baseline.
Conclusion: Management of HIV-infected, opioid-dependent patients with a clinic-based BUP strategy facilitates access to opioid agonist therapy and improves outcomes of substance abuse treatment.
Primary funding source: Health Resources and Services Administration Special Projects of National Significance program.
Figures
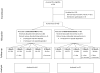

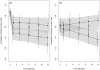
References
-
- Fiellin DA, O’Connor PG. New federal initiatives to enhance the medical treatment of opioid dependence. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(8):688–692. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Peachey JE, Lei H. Assessment of opioid dependence with naloxone. Br J Addict. 1988;83(2):193–201. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Substance Abuse Treatment. Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series 40. DHHS Publication No. (SMA) 04-3939. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2004. Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine in the Treatment of Opioid Addiction. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01AI071754/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DA015616/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA011602/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA025991/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AA016893/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA019511/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA025991/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018577/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI071754/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA020576/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24DA000432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA018577/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA019511/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23DA015616/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020576/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
