Effects of arsenic exposure on DNA methylation and epigenetic gene regulation
- PMID: 20514360
- PMCID: PMC2877392
- DOI: 10.2217/epi.09.45
Effects of arsenic exposure on DNA methylation and epigenetic gene regulation
Abstract
Arsenic is a nonmutagenic human carcinogen that induces tumors through unknown mechanisms. A growing body of evidence suggests that its carcinogenicity results from epigenetic changes, particularly in DNA methylation. Changes in gene methylation status, mediated by arsenic, have been proposed to activate oncogene expression or silence tumor suppressor genes, leading to long-term changes in the activity of genes controlling cell transformation. Mostly descriptive, and often contradictory, studies have demonstrated that arsenic exposure is associated with both hypo- and hyper-methylation at various genetic loci in vivo or in vitro. This ambiguity has made it difficult to assess whether the changes induced by arsenic are causally involved in the transformation process or are simply a reflection of the altered physiology of rapidly dividing cancer cells. Here, we discuss the evidence supporting changes in DNA methylation as a cause of arsenic carcinogenesis and highlight the strengths and limitations of these studies, as well as areas where consistencies and inconsistencies exist.
Keywords: DNMT; S-adenosylmethionine; SAM; arsenate; arsenic; arsenite; cancer; carcinogenesis; epigenetics; glutathione; hypermethylation; hypomethylation; oxidative stress; transsulfuration.
Figures

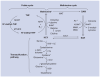
References
Bibliography
-
- Chen CJ, Kuo TL, Wu MM. Arsenic and cancers. Lancet. 1988;1(8582):414–415. - PubMed
-
- Hopenhayn-Rich C, Biggs ML, Fuchs A, et al. Bladder cancer mortality associated with arsenic in drinking water in Argentina. Epidemiology. 1996;7(2):117–124. - PubMed
-
- Marshall G, Ferreccio C, Yuan Y, et al. Fifty-year study of lung and bladder cancer mortality in Chile related to arsenic in drinking water. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(12):920–928. - PubMed
■ Websites
-
- IARC . Some Drinking-Water Disinfectants and Contaminants, Including Arsenic. Vol. 84. Who Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2004. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Human IARC Monographs. ISBN-13 9789283212843, ISBN-10 9283212843. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol84/index.php. - PMC - PubMed
-
- ATSDR . Toxicological Profile for Arsenic. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service; GA, USA: 2007. Toxicological profile for Arsenic. www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp2.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
