Pre-operative intracellular glutathione levels of peripheral monocytes as a biomarker to predict survival of colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 20514541
- PMCID: PMC11030285
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0868-3
Pre-operative intracellular glutathione levels of peripheral monocytes as a biomarker to predict survival of colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
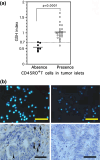
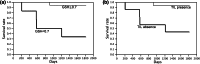
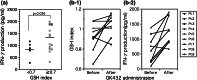
The ability to predict anti-tumor immune responses at local tumor growing sites using only peripheral blood specimens would be helpful in determining therapeutic options for patients with solid tumors. Here, we show that the glutathione intracellular content (icGSH) of peripheral monocytes (Mo) correlates positively with T cell infiltration within tumor islets and overall survival in patients with colorectal carcinoma. IcGSH redox status was determined in CD14(+) Mo prior to surgery by staining with monochlorobimane. The tumor-infiltrating T cells (TIL) were quantified as CD45RO(+) T cells in resected tumors using paraffin sections. A positive association was found between the GSH index and TIL in tumor islets (P < 0.001). The 50% cut-off value for the GSH index, that is the determinant between TIL presence or absence in tumor islets, was calculated to be almost 0.7 through logistic regression analysis. Mo with a GSH index of > or =0.7 were termed reductive (R)-Mo, and those with <0.7 were designated as oxidative (O)-Mo. Cox's proportional hazards regression analysis of patients with R-Mo or O-Mo prior to surgery, and the presence or absence of TIL, was found to correlate significantly with the overall survival rate of stage II and III patients. Kaplan-Meier analysis also showed a significant correlation. These results indicate that the Mo icGSH index is a useful biomarker parameter for better understanding the host/tumor relationship prior to surgery, thereby enabling the development of an individual patient-oriented therapeutic strategy.
Figures
References
-
- Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Schioppa T, Saccani A, et al. Infiltration of tumours by macrophages and dendritic cells: tumour-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;256:137–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

