Genetic modification of ex-vivo expanded stem cells for clinical application
- PMID: 20515730
- PMCID: PMC9930440
- DOI: 10.2741/3650
Genetic modification of ex-vivo expanded stem cells for clinical application
Abstract
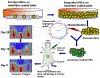
Stem cell therapy is currently considered as an important regime for repairing, replacing or enhancing the biological functions of the damaged tissues. Among adult stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are commonly used for cure of hematological disorders. However, the number of HSCs obtained from sources like bone marrow, peripheral or umbilical cord blood is not sufficient for routine clinical application. Thus, ex-vivo expansion of HSCs becomes critically important. Ex-vivo culture and expansion of stem cells are challenging, as stem cells differentiate in culture rather than self-renew. Lack of clarity about the factors responsible for quiescence and differentiation of HSCs, investigators struggled to optimize conditions for ex vivo expansion. As we understand better, various strategies can be incorporated to mimic in vivo conditions for successful expansion of stem cells. However, characterization and biological functionality should also be tested for expanded stem cells prior to clinical application. To treat ischemia by enhancing therapeutic angiogenesis and neo-vascularization, the role of genetic modification of HSCs with pro-angiogenic factors is the focus of this review.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hematopoietic stem cells: transcriptional regulation, ex vivo expansion and clinical application.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jan;12(1):34-49. doi: 10.2174/156652412798376125. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22082480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in hematopoietic stem cells ex vivo expansion associated with bone marrow niche.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):5035-5057. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05773-1. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38684510 Review.
-
Angiopoietin-like protein 3 promotes preservation of stemness during ex vivo expansion of murine hematopoietic stem cells.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e105642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105642. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25170927 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Cytokine Conditions Reveals Resveratrol as a New Molecule for Ex Vivo Cultivation of Cord Blood-Derived Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015 Sep;4(9):1064-72. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0284. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26160960 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant TAT-BMI-1 fusion protein induces ex vivo expansion of human umbilical cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 4;8(27):43782-43798. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15156. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28187462 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hematopoietic stem cells: transcriptional regulation, ex vivo expansion and clinical application.Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jan;12(1):34-49. doi: 10.2174/156652412798376125. Curr Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22082480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient, long term production of monocyte-derived macrophages from human pluripotent stem cells under partly-defined and fully-defined conditions.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 12;8(8):e71098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071098. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951090 Free PMC article.
-
The quest for the holy grail: overcoming challenges in expanding human hematopoietic stem cells for clinical use.Stem Cell Investig. 2023 Jul 11;10:15. doi: 10.21037/sci-2023-016. eCollection 2023. Stem Cell Investig. 2023. PMID: 37457748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-viral Gene Delivery Methods for Bone and Joints.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Nov 19;8:598466. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.598466. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33330428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neovascularization and hematopoietic stem cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013 Nov;67(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s12013-011-9298-x. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 22038301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Price J and Williams BP: Neural stem cells. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 11(5), 564–7 (2001) - PubMed
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS and Jones JM: Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science, 282(5391), 1145–7 (1998) - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell, 131(5), 861–72 (2007) - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell, 126(4), 663–76 (2006) - PubMed
-
- Wernig M, Meissner A, Cassady JP and Jaenisch R: c-Myc is dispensable for direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell, 2(1), 10–2 (2008) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

