Gene expression and transcription factor profiling reveal inhibition of transcription factor cAMP-response element-binding protein by gamma-herpesvirus replication and transcription activator
- PMID: 20516076
- PMCID: PMC2919076
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137737
Gene expression and transcription factor profiling reveal inhibition of transcription factor cAMP-response element-binding protein by gamma-herpesvirus replication and transcription activator
Abstract
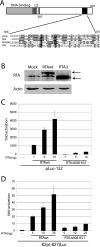
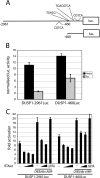
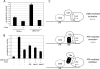
Herpesvirus replication involves the expression of over 80 viral genes in a well ordered sequence, leading to the production of new virions. Viral genes expressed during the earliest phases of replication often regulate both viral and cellular genes. Therefore, they have the potential to bring about dramatic functional changes within the cell. Replication and transcription activator (RTA) is a potent immediate early transcription activator of the gamma-herpesvirus family. This family includes Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, human pathogens associated with malignancy. Here we combine gene array technology with transcription factor profiling to identify the earliest DNA promoter and cellular transcription factor targets of RTA in the cellular genome. We find that expression of RTA leads to both activation and inhibition of distinct groups of cellular genes. The identity of the target genes suggests that RTA rapidly changes the cellular environment to counteract cell death pathways, support growth factor signaling, and also promote immune evasion of the infected cell. Transcription factor profiling of the target gene promoters highlighted distinct pathways involved in gene activation at specific time points. Most notable throughout was the high level of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB)-response elements in RTA target genes. We find that RTA can function as either an activator or an inhibitor of CREB-response genes, depending on the promoter context. The association with CREB also highlights a novel connection and coordination between viral and cellular "immediate early" responses.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of a new Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus replication and transcription activator (RTA)-responsive element involved in RTA-mediated transactivation.J Gen Virol. 2009 Apr;90(Pt 4):944-953. doi: 10.1099/vir.2008.006817-0. Epub 2009 Feb 17. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19223488 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Orf50 Transcripts: Discovery of New RTA Isoforms with Variable Transactivation Potential.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01434-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01434-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795414 Free PMC article.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
-
Regulation of primary response genes.Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 4;44(3):348-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.014. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22055182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ser-634 and Ser-636 of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus RTA are Involved in Transactivation and are Potential Cdk9 Phosphorylation Sites.Front Microbiol. 2012 Feb 22;3:60. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00060. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22371709 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in leukocyte transcriptional control pathway activity associated with major depressive disorder and antidepressant treatment.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 May 24;6(5):e821. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.79. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27219347 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of the Human Kinome Identifies MSK1/2-CREB1 as an Essential Pathway Mediating Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication during Primary Infection.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(18):9262-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01098-15. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26109721 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium and GADL1 regulate glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity to modulate KCTD12 expression.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 16;9(1):10255. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46655-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31311980 Free PMC article.
-
Daily heart rate variability biofeedback training decreases locus coeruleus MRI contrast in younger adults in a randomized clinical trial.Int J Psychophysiol. 2023 Nov;193:112241. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2023.08.014. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Int J Psychophysiol. 2023. PMID: 37647944 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rickinson A. B., Kieff E. (2001) in Fields Virology, 4th Ed., pp. 2817–2818, (Knipe D. M., Howley P. M. eds) Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
-
- Burke A. P., Yen T. S., Shekitka K. M., Sobin L. H. (1990) Mod. Pathol. 3, 377–380 - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E., Chang Y., Moore P. S., Said J. W., Knowles D. M. (1995) N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1186–1191 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

