Breast cancer cells in three-dimensional culture display an enhanced radioresponse after coordinate targeting of integrin alpha5beta1 and fibronectin
- PMID: 20516121
- PMCID: PMC2933183
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2319
Breast cancer cells in three-dimensional culture display an enhanced radioresponse after coordinate targeting of integrin alpha5beta1 and fibronectin
Abstract
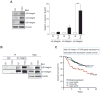
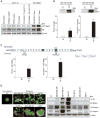
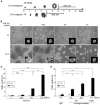
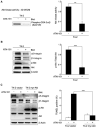
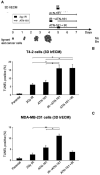
Tactics to selectively enhance cancer radioresponse are of great interest. Cancer cells actively elaborate and remodel their extracellular matrix (ECM) to aid in survival and progression. Previous work has shown that beta1-integrin inhibitory antibodies can enhance the growth-inhibitory and apoptotic responses of human breast cancer cell lines to ionizing radiation, either when cells are cultured in three-dimensional laminin-rich ECM (3D lrECM) or grown as xenografts in mice. Here, we show that a specific alpha heterodimer of beta1-integrin preferentially mediates a prosurvival signal in human breast cancer cells that can be specifically targeted for therapy. 3D lrECM culture conditions were used to compare alpha-integrin heterodimer expression in malignant and nonmalignant cell lines. Under these conditions, we found that expression of alpha5beta1-integrin was upregulated in malignant cells compared with nonmalignant breast cells. Similarly, we found that normal and oncofetal splice variants of fibronectin, the primary ECM ligand of alpha5beta1-integrin, were also strikingly upregulated in malignant cell lines compared with nonmalignant acini. Cell treatment with a peptide that disrupts the interactions of alpha5beta1-integrin with fibronectin promoted apoptosis in malignant cells and further heightened the apoptotic effects of radiation. In support of these results, an analysis of gene expression array data from breast cancer patients revealed an association of high levels of alpha5-integrin expression with decreased survival. Our findings offer preclinical validation of fibronectin and alpha5beta1-integrin as targets for breast cancer therapy.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Yao ES, Zhang H, Chen YY, et al. Increased β1 integrin is associated with decreased survival in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:659–64. - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–87. - PubMed
-
- Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987;238:491–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA126552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA126552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA124891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

